Stability and reproducibility of 6013 deep inspiration breath-holds in left-sided breast cancer
- PMID: 32448224
- PMCID: PMC7247126
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-020-01572-w
Stability and reproducibility of 6013 deep inspiration breath-holds in left-sided breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Patients with left-sided breast cancer frequently receive deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) radiotherapy to reduce the risk of cardiac side effects. The aim of the present study was to analyze intra-breath-hold stability and inter-fraction breath-hold reproducibility in clinical practice.
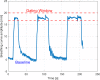
Material and methods: Overall, we analyzed 103 patients receiving left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy using a surface-guided DIBH technique. During each treatment session the vertical motion of the patient was continuously measured by a surface guided radiation therapy (SGRT) system and automated gating control (beam on/off) was performed using an audio-visual patient feedback system. Dose delivery was automatically triggered when the tracking point was within a predefined gating window. Intra-breath-hold stability and inter-fraction reproducibility across all fractions of the entire treatment course were analyzed per patient.
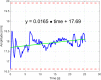
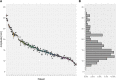
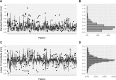
Results: In the present series, 6013 breath-holds during beam-on time were analyzed. The mean amplitude of the gating window from the baseline breathing curve (maximum expiration during free breathing) was 15.8 mm (95%-confidence interval: [8.5-30.6] mm) and had a width of 3.5 mm (95%-CI: [2-4.3] mm). As a measure of intra-breath-hold stability, the median standard deviation of the breath-hold level during DIBH was 0.3 mm (95%-CI: [0.1-0.9] mm). Similarly, the median absolute intra-breath-hold linear amplitude deviation was 0.4 mm (95%-CI: [0.01-2.1] mm). Reproducibility testing showed good inter-fractional reliability, as the maximum difference in the breathing amplitudes in all patients and all fractions were 1.3 mm on average (95%-CI: [0.5-2.6] mm).
Conclusion: The clinical integration of an optical surface scanner enables a stable and reliable DIBH treatment delivery during SGRT for left-sided breast cancer in clinical routine.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DIBH; Inter-fraction; Intra-breath-hold; Optical surface scanner; Reproducibility; Stability; Surface guided radiation therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
CB, PF received research grants and MR, SC, PF speaker honoraria from C-RAD. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Setup margins based on the inter- and intrafractional setup error of left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy using deep inspiration breath-hold technique (DIBH) and surface guided radiotherapy (SGRT).J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jun;25(6):e14271. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14271. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38273673 Free PMC article.
-
Reproducibility and stability of spirometer-guided deep inspiration breath-hold in left-breast treatments using an optical surface monitoring system.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 Jun;24(6):e13922. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13922. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36852489 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment planning and evaluation of gated radiotherapy in left-sided breast cancer patients using the CatalystTM/SentinelTM system for deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH).Radiat Oncol. 2016 Oct 26;11(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0716-5. Radiat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27784326 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac dose comparison of abdominal and thoracic deep inspiration breath hold in adult female with left-sided breast cancer receiving radiation therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Radiography (Lond). 2025 Jan;31(1):426-433. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2024.12.013. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Radiography (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39779416
-
Deep Inspiration Breath Hold-Based Radiation Therapy: A Clinical Review.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Mar 1;94(3):478-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.11.049. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26867877 Review.
Cited by
-
Setup margins based on the inter- and intrafractional setup error of left-sided breast cancer radiotherapy using deep inspiration breath-hold technique (DIBH) and surface guided radiotherapy (SGRT).J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jun;25(6):e14271. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14271. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38273673 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Pitfall and Clinical Solutions in Surface-Guided Deep Inspiration Breath Hold Radiation Therapy for Left-Sided Breast Cancer.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023 May 27;8(6):101276. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101276. eCollection 2023 Nov-Dec. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38047221 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of patient setup accuracy for optical surface-guided and X-ray-guided imaging with respect to the impact on intracranial stereotactic radiotherapy.Strahlenther Onkol. 2024 Jan;200(1):60-70. doi: 10.1007/s00066-023-02170-x. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Strahlenther Onkol. 2024. PMID: 37971534
-
Automated hybrid volumetric modulated arc therapy (HVMAT) for whole-breast irradiation with simultaneous integrated boost to lumpectomy area : A treatment planning study.Strahlenther Onkol. 2022 Mar;198(3):254-267. doi: 10.1007/s00066-021-01873-3. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Strahlenther Onkol. 2022. PMID: 34767044
-
New patient setup procedure using surface-guided imaging to reduce body touch and skin marks in whole-breast irradiation during the COVID-19 pandemic.Radiol Phys Technol. 2023 Sep;16(3):422-429. doi: 10.1007/s12194-023-00735-0. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Radiol Phys Technol. 2023. PMID: 37474738
References
-
- Schönecker S, Walter F, Freislederer P, et al. Treatment planning and evaluation of gated radiotherapy in left-sided breast cancer patients using the catalyst(TM)/sentinel(TM) system for deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) Radiat Oncol. 2016;11(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0716-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

