Assessing the reporting quality of physical activity programs in randomized controlled trials for the management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis using three standardized assessment tools
- PMID: 32448277
- PMCID: PMC7245815
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-020-00434-9
Assessing the reporting quality of physical activity programs in randomized controlled trials for the management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis using three standardized assessment tools
Abstract
Background: The reporting quality of physical activity (PA) programs in randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for the management of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) remains unknown. This study aimed to assess and compare the reporting quality of PA programs in RCTs for the management of JIA using three difference standardized assessment tools, and to describe the elements that were similar and different between these tools.
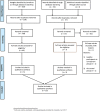
Methods: A systematic search was conducted for moderate-to high-quality RCTs of PA programs in JIA, published up until January 2019. Two reviewers independently included 10 RCTs and scored the reporting quality of PA programs using the following tools: Consensus on Exercise Reporting Template (CERT) checklist, Consensus on Therapeutic Exercise Training (CONTENT) scale, and Template for Intervention Description and Replication (TIDieR) checklist.
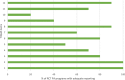
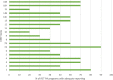
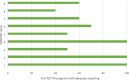
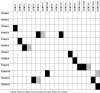
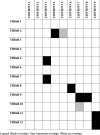
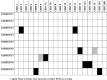
Results: Results showed that reporting of PA programs in 10 moderate- to high-quality RCTs for JIA management remains incomplete. The average reporting quality (± standard deviation) for all RCTs combined was moderate for the three standardized assessment tools with 70.8 (±14.3)% for the TIDieR checklist, 53.2 (±20.2)% for the CERT checklist, and 70.0 (±18.9)% for the CONTENT scale. Despite some overlap, the three standardized assessment tools (TIDieR, CERT, CONTENT) included different elements resulting in different scores. All tools assess elements linked to PA programs (provider, location, timing, personalization and adherence), but the CERT checklist includes other essential elements (e.g., additional resources, motivational strategies, adverse events).
Conclusions: The lack of complete reporting of PA programs in RCTs for the management of JIA and the variation in scores and assessed elements among standardized assessment tools show the need to improve reporting. Using the most comprehensive standardized tool (i.e., the CERT) and providing accessible supplemental information on PA programs may improve the reporting quality of PA programs in RCTs and help reproduce PA programs in research and clinical practice.
Keywords: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis; Physical activity programs; Randomized controlled trials; Reporting quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. Dr. Lucie Brosseau was an author on the publication describing the development of the CERT checklist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intervention reporting and dissemination of information for the management of hand osteoarthritis.J Hand Ther. 2021 Jul-Sep;34(3):362-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jht.2020.03.020. Epub 2020 Jun 18. J Hand Ther. 2021. PMID: 32565101
-
The management of lower back pain using pilates method: assessment of content exercise reporting in RCTs.Disabil Rehabil. 2022 Jun;44(11):2428-2436. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2020.1836269. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Disabil Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 33096012 Review.
-
How well do published randomized controlled trials on pelvic floor muscle training interventions for urinary incontinence describe the details of the intervention? A review.Neurourol Urodyn. 2020 Jan;39(1):35-44. doi: 10.1002/nau.24208. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Neurourol Urodyn. 2020. PMID: 31692078 Review.
-
Ottawa Panel Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Structured Physical Activity in the Management of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017 May;98(5):1018-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2016.09.135. Epub 2016 Dec 6. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017. PMID: 27932265 Review.
-
Assessment of the completeness of intervention reporting of randomized clinical trials for alcohol use disorders: Effect of the TIDieR checklist and guide.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020 Mar 1;208:107824. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.107824. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2020. PMID: 32014645 Review.
Cited by
-
Reporting quality of interventions using a wearable activity tracker to improve physical activity in patients with inflammatory arthritis or osteoarthritis: a systematic review.Rheumatol Int. 2023 May;43(5):803-824. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05241-x. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Rheumatol Int. 2023. PMID: 36454326 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of YouTube-Based Therapeutic Content for Children with Cerebral Palsy.Children (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;11(7):814. doi: 10.3390/children11070814. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062263 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Early Physical Therapy Rehabilitation in Patient With Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis.Cureus. 2022 Oct 12;14(10):e30213. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30213. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36381930 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Training Interventions for Lower Limb Tendinopathies: A Scoping Review of Resistance Training Reporting Content, Quality, and Scientific Implementation.Transl Sports Med. 2022 Mar 10;2022:2561142. doi: 10.1155/2022/2561142. eCollection 2022. Transl Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 38655173 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Analysis of YouTube-Based Exercise Programs for Typically Developing Children: Content Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Mar 5;13(5):560. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050560. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schanberg LE, Anthony KK, Gil KM, Maurin EC. Daily pain and symptoms in children with polyarticular arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(5):1390–1397. - PubMed
-
- Petty R, Laxer R, Lindsley C, Wedderburn L. Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2015.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

