Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients: diagnostic reliability of HLH-2004 criteria and HScore
- PMID: 32448380
- PMCID: PMC7245825
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-02941-3
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients: diagnostic reliability of HLH-2004 criteria and HScore
Abstract
Background: Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare though often fatal hyperinflammatory syndrome mimicking sepsis in the critically ill. Diagnosis relies on the HLH-2004 criteria and HScore, both of which have been developed in pediatric or adult non-critically ill patients, respectively. Therefore, we aimed to determine the sensitivity and specificity of HLH-2004 criteria and HScore in a cohort of adult critically ill patients.
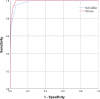
Methods: In this further analysis of a retrospective observational study, patients ≥ 18 years admitted to at least one adult ICU at Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin between January 2006 and August 2018 with hyperferritinemia of ≥ 500 μg/L were included. Patients' charts were reviewed for clinically diagnosed or suspected HLH. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was performed to determine prediction accuracy.
Results: In total, 2623 patients with hyperferritinemia were included, of whom 40 patients had HLH. We found the best prediction accuracy of HLH diagnosis for a cutoff of 4 fulfilled HLH-2004 criteria (95.0% sensitivity and 93.6% specificity) and HScore cutoff of 168 (100% sensitivity and 94.1% specificity). By adjusting HLH-2004 criteria cutoffs of both hyperferritinemia to 3000 μg/L and fever to 38.2 °C, sensitivity and specificity increased to 97.5% and 96.1%, respectively. Both a higher number of fulfilled HLH-2004 criteria [OR 1.513 (95% CI 1.372-1.667); p < 0.001] and a higher HScore [OR 1.011 (95% CI 1.009-1.013); p < 0.001] were significantly associated with in-hospital mortality.
Conclusions: An HScore cutoff of 168 revealed a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 94.1%, thereby providing slightly superior diagnostic accuracy compared to HLH-2004 criteria. Both HLH-2004 criteria and HScore proved to be of good diagnostic accuracy and consequently might be used for HLH diagnosis in critically ill patients.
Clinical trial registration: The study was registered with www.ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02854943) on August 1, 2016.
Keywords: Diagnosis; HLH-2004 criteria; HScore; Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH); Hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS); Intensive care unit (ICU); Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Knaak Cornelia, Schuster Friederike S., Spies Claudia, Vorderwülbecke Gerald, Nyvlt Peter, Schenk Thomas, Balzer Felix, La Rosée Paul, Janka Gritta, Brunkhorst Frank M., Keh Didier, Lachmann Gunnar. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Critically Ill Patients. SHOCK. 2020;53(6):701–709. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001454. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical