Efficacy and safety of tisagenlecleucel in Japanese adult patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 32448949
- PMCID: PMC7441082
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-020-01699-6
Efficacy and safety of tisagenlecleucel in Japanese adult patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Tisagenlecleucel demonstrated a high rate of durable response in adult patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in the pivotal global phase 2 JULIET study. Here, we report the efficacy and safety of tisagenlecleucel in the Japanese subgroup.
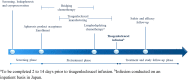
Methods: JULIET (NCT02445248) is a single-arm, open-label, multicenter, phase 2 study involving adult patients with r/r DLBCL who either relapsed after or were ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant. Primary endpoint was best overall response rate (ORR; complete response [CR] + partial response [PR]) as judged by an independent review committee.
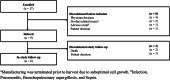
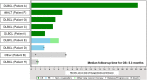
Results: In Japan, of 17 patients enrolled, 9 were infused with tisagenlecleucel and completed ≥ 3 months of follow-up. Best ORR was 77.8% (7/9; 95% confidence interval, 40.0-97.2), with 5 patients (55.6%) in CR and 2 (22.2%) in PR. Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 6 patients (66.7%), with grade 3 CRS in 2 patients (Penn grading scale). Two patients received tocilizumab. Two deaths (22.2%) occurred more than 30 days after tisagenlecleucel infusion due to disease progression, neither of which were related to tisagenlecleucel.
Conclusion: Tisagenlecleucel showed a high best ORR with a manageable safety profile, thus offering a new treatment option in selected Japanese patients with r/r DLBCL.
Keywords: CAR T-cell therapy; Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; JULIET; Tisagenlecleucel.
Conflict of interest statement
S.M. received personal fees from Novartis, Takeda, Eisai, Daiichi Sankyo, and Celgene. K.A. reports research grants from Novartis, MSD, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas, AbbVie, Alexion, Chemo-Sero-Therapeutic Research Institute, Japan Blood Products Organization, Eisai, Otsuka, Ono, Yakult, Shin Nippon Biomedical Laboratories, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Sanofi, Shionogi, Daiichi Sankyo, Taisho, Dainippon Sumitomo, Taiho, Takeda, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Chugai, Teijin, FUJIFILM Toyoma Chemical, Eli Lilly, Nippon Kayaku, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mundipharma, Merck, Mochida, and Nihon Pharmaceutical, and personal fees from Novartis, CSL Behring, MSD, Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas Amgen, Astellas, AbbVie, Alexion, Eisai, Otsuka, Ono, Medical Review, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Sanofi, Shionogi, Shire Japan, SymBio, Celgene, Daiichi Sankyo, Taisho, Dainippon Sumitomo, Takeda, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Chugai, Teijin, Nippon Shinyaku, Eli Lilly, Bayer, Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Mundi Pharma, Mochida, and Janssen. K.I. reports research grants from Novartis, Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, MSD, Takeda, Janssen, Mundipharma, Chugai, AbbVie, Bayer, Ono, Gilead, Zenyaku, Celgene, Solasia, Symbio, Astellas, Astellas Amgen, and Daiichi Sankyo, and personal fees from Kyowa Hakko Kirin, MSD, Takeda, Janssen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Dainippon Sumitomo, Mundipharma, Nihon Mediphysics, Chugai, Astra Zeneca, AbbVie, Bayer, Ono, and Celgene. T.T. reports research grants and personal fees from Novartis. K.T. and T.F. are employees of Novartis. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

