Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL37 Inhibits T Cell-dependent Immune Response in Mice
- PMID: 32448979
- PMCID: PMC7246254
- DOI: 10.1007/s00005-020-00581-7
Exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL37 Inhibits T Cell-dependent Immune Response in Mice
Abstract
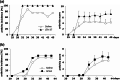
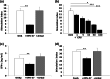
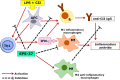
Exopolysaccharides (EPSs), major components of the bacterial biofilm, display strong strain-specific immunomodulatory properties. Previously, we have shown that crude EPS derived from Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL37 depresses the production of arthritogenic anti-collagen IgG and ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1 mice, when lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as adjuvant. In this study, we used highly purified EPS from L. rhamnosus KL37 (EPS-37) to verify its anti-inflammatory properties and the ability to suppress T cell-dependent humoral response. We have employed the model of active CIA, in which mice immunized with type II collagen (CII) along with LPS were treated with pure EPS-37. Intravenous administration of purified EPS-37 markedly ameliorated arthritis and reduced CII-specific antibody production. EPS-37 injected subcutaneously reduced the clinical symptoms of CIA but without the reduction of arthritogenic antibodies. In addition, the effect of EPS-37 on T-cell functions was tested ex vivo and in vitro. EPS-37 inhibited the in vitro proliferation of T cells activated both in vivo (CII immunization) and in vitro (antigen/mitogen), and markedly reduced the production of interferon (IFN)-γ. These results together with other reports suggest that anti-inflammatory potential of EPS-37 depends on its ability to inhibit either one or the other or both possible inflammatory signaling pathways. Namely, Th1 → IFN-γ → M1 inflammatory macrophages → arthritis and/or Th1 → IFN-γ → B cells → arthritogenic antibodies → arthritis. We suggest that L. rhamnosus KL37 EPS might be utilized to control T cell-dependent immune responses in various inflammatory diseases. However, the most effective route of EPS-37 administration needs to be tailored for a given disorder.
Keywords: Collagen-induced arthritis; Exopolysaccharide; Immunomodulation; Inflammation; Lactobacillus rhamnosus; T cells.
Figures




References
-
- Brand DD, Kang AH, Rosloniec EF. Immunopathogenesis of collagen arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2003;25:3–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

