Hepatitis B virus cccDNA: Formation, regulation and therapeutic potential
- PMID: 32450266
- PMCID: PMC7387223
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104824
Hepatitis B virus cccDNA: Formation, regulation and therapeutic potential
Abstract
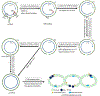
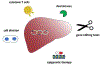
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a major public health concern worldwide with about 257 million individuals chronically infected. Current therapies can effectively control HBV replication and slow down disease progress, but cannot cure HBV infection. Upon infection, HBV establishes a pool of covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) in the nucleus of infected hepatocytes. The cccDNA exists as a minichromosome and resists to antivirals, thus a therapeutic eradication of cccDNA from the infected cells remains unattainable. In this review, we summarize the state of knowledge on the mechanisms underlying cccDNA formation and regulation, and discuss the possible strategies that may contribute to the eradication of HBV through targeting cccDNA.
Keywords: Drug target; HBV cccDNA minichromosome; HBV cure; Host-virus interaction; Transcriptional regulation; cccDNA eradication.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Allweiss L, Volz T, Giersch K, Kah J, Raffa G, Petersen J, Lohse AW, Beninati C, Pollicino T, Urban S, Lutgehetmann M, Dandri M, 2018. Proliferation of primary human hepatocytes and prevention of hepatitis B virus reinfection efficiently deplete nuclear cccDNA in vivo. Gut 67, 542–552. - PubMed
-
- Allweiss L, Volz T, Lutgehetmann M, Giersch K, Bornscheuer T, Lohse AW, Petersen J, Ma H, Klumpp K, Fletcher SP, Dandri M, 2014. Immune cell responses are not required to induce substantial hepatitis B virus antigen decline during pegylated interferon-alpha administration. J Hepatol 60, 500–507. - PubMed
-
- Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F, Pediconi N, Volz T, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Raimondo G, Dandri M, Levrero M, 2012. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. The Journal of clinical investigation 122, 529–537. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belloni L, Pollicino T, De Nicola F, Guerrieri F, Raffa G, Fanciulli M, Raimondo G, Levrero M, 2009. Nuclear HBx binds the HBV minichromosome and modifies the epigenetic regulation of cccDNA function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106, 19975–19979. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

