Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe
- PMID: 32450906
- PMCID: PMC7247289
- DOI: 10.1186/s13293-020-00304-9
Impact of sex and gender on COVID-19 outcomes in Europe
Abstract
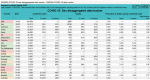
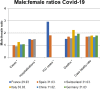
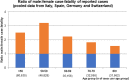
Background: Emerging evidence from China suggests that coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is deadlier for infected men than women with a 2.8% fatality rate being reported in Chinese men versus 1.7% in women. Further, sex-disaggregated data for COVID-19 in several European countries show a similar number of cases between the sexes, but more severe outcomes in aged men. Case fatality is highest in men with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions. The mechanisms accounting for the reduced case fatality rate in women are currently unclear but may offer potential to develop novel risk stratification tools and therapeutic options for women and men.
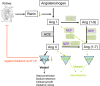
Content: The present review summarizes latest clinical and epidemiological evidence for gender and sex differences in COVID-19 from Europe and China. We discuss potential sex-specific mechanisms modulating the course of disease, such as hormone-regulated expression of genes encoding for the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) entry receptors angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) 2 receptor and TMPRSS2 as well as sex hormone-driven innate and adaptive immune responses and immunoaging. Finally, we elucidate the impact of gender-specific lifestyle, health behavior, psychological stress, and socioeconomic conditions on COVID-19 and discuss sex specific aspects of antiviral therapies.
Conclusion: The sex and gender disparities observed in COVID-19 vulnerability emphasize the need to better understand the impact of sex and gender on incidence and case fatality of the disease and to tailor treatment according to sex and gender. The ongoing and planned prophylactic and therapeutic treatment studies must include prospective sex- and gender-sensitive analyses.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gender; Immune system; Renin angiotensin aldosterone system; Sex.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared
Figures
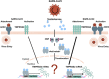
References
-
- Guan Wei-jie, Ni Zheng-yi, Hu Yu, Liang Wen-hua, Ou Chun-quan, He Jian-xing, Liu Lei, Shan Hong, Lei Chun-liang, Hui David S.C., Du Bin, Li Lan-juan, Zeng Guang, Yuen Kwok-Yung, Chen Ru-chong, Tang Chun-li, Wang Tao, Chen Ping-yan, Xiang Jie, Li Shi-yue, Wang Jin-lin, Liang Zi-jing, Peng Yi-xiang, Wei Li, Liu Yong, Hu Ya-hua, Peng Peng, Wang Jian-ming, Liu Ji-yang, Chen Zhong, Li Gang, Zheng Zhi-jian, Qiu Shao-qin, Luo Jie, Ye Chang-jiang, Zhu Shao-yong, Zhong Nan-shan. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382(18):1708–1720. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Who director-general’s opening remarks at the media briefing on Covid-19 - 11 March 2020. 2020. World Health Organisation. https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re... (Date accessed:22.03.2020).
-
- Coronarvirus Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University Medicine. 2020. Johns Hopkins University Medicine. Medicine JHU. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (Date accessed:22.03.2020).
-
- Roche to start phase III trial of actemra in Covid-19 patients. 2020. https://www.clinicaltrialsarena.com/news/roche-actemra-covid-19-trial/ (Date accessed:22.03.2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Research grant/Olga Mayenfisch Foundation, Switzerland/International
- Research grant/Schweizerische Herzstiftung/International
- Research grant/University Hospital Zurich Foundation, Switzerland/International
- Research grant/Schweizerischer Nationalfonds zur Förderung der Wissenschaftlichen Forschung/International
- Research grant/EMDO Foundation, Switzerland/International
- Research grant/Helmut Horten Foundation, Switzerland/International
- Research grant/Novartis Stiftung für Medizinisch-Biologische Forschung/International
- Research grant/Iten-Kohaut Foundation, Switzerland/International
- U54 AG062333/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Research grant/OPO Foundation, Switzerland/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

