COVID-19 under spotlight: A close look at the origin, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of the 2019-nCoV disease
- PMID: 32452539
- PMCID: PMC7283670
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29735
COVID-19 under spotlight: A close look at the origin, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of the 2019-nCoV disease
Abstract
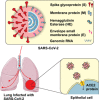
Months after the outbreak of a new flu-like disease in China, the entire world is now in a state of caution. The subsequent less-anticipated propagation of the novel coronavirus disease, formally known as COVID-19, not only made it to headlines by an overwhelmingly high transmission rate and fatality reports, but also raised an alarm for the medical community all around the globe. Since the causative agent, SARS-CoV-2, is a recently discovered species, there is no specific medicine for downright treatment of the infection. This has led to an unprecedented societal fear of the newly born disease, adding a psychological aspect to the physical manifestation of the virus. Herein, the COVID-19 structure, epidemiology, pathogenesis, etiology, diagnosis, and therapy have been reviewed.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV or COVID-19 or SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; epidemiology; etiology; pathogenesis; therapy.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Agarwal, H. K. , Chhikara, B. S. , Doncel, G. F. , & Parang, K. (2017). Synthesis and anti‐HIV activities of unsymmetrical long chain dicarboxylate esters of dinucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 27(9), 1934–1937. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal, H. K. , Chhikara, B. S. , Quiterio, M. , Doncel, G. F. , & Parang, K. (2012). Synthesis and anti‐HIV activities of glutamate and peptide conjugates of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 55(6), 2672–2687. - PubMed
-
- Ai, T. , Yang, Z. , Hou, H. , Zhan, C. , Chen, C. , Lv, W. , & Xia, L. (2020). Correlation of chest CT and RT‐PCR testing in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) in China: A report of 1014 cases. Radiology, 200642, 1–23. https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.2020200642 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azhar, E. , & EI‐Kafrawy, S. (2014). Evidence for camel‐to‐human transmission of MERS coronavirus. New England Journal of Medicine, 370(26), 2499–2505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous