Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Type I Interferon Promote Extrafollicular B Cell Responses to Extracellular Self-DNA
- PMID: 32454024
- PMCID: PMC7306002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.015
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Type I Interferon Promote Extrafollicular B Cell Responses to Extracellular Self-DNA
Abstract
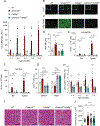
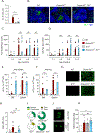
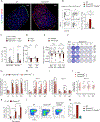
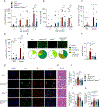
Class-switched antibodies to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) are prevalent and pathogenic in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), yet mechanisms of their development remain poorly understood. Humans and mice lacking secreted DNase DNASE1L3 develop rapid anti-dsDNA antibody responses and SLE-like disease. We report that anti-DNA responses in Dnase1l3-/- mice require CD40L-mediated T cell help, but proceed independently of germinal center formation via short-lived antibody-forming cells (AFCs) localized to extrafollicular regions. Type I interferon (IFN-I) signaling and IFN-I-producing plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) facilitate the differentiation of DNA-reactive AFCs in vivo and in vitro and are required for downstream manifestations of autoimmunity. Moreover, the endosomal DNA sensor TLR9 promotes anti-dsDNA responses and SLE-like disease in Dnase1l3-/- mice redundantly with another nucleic acid-sensing receptor, TLR7. These results establish extrafollicular B cell differentiation into short-lived AFCs as a key mechanism of anti-DNA autoreactivity and reveal a major contribution of pDCs, endosomal Toll-like receptors (TLRs), and IFN-I to this pathway.
Keywords: DNASE1L3; TLR7; TLR9; anti-DNA antibodies; extrafollicular B cell response; plasmacytoid dendritic cells; systemic lupus erythematosus; type I interferon.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal H, Jacob N, Carreras E, Bajana S, Putterman C, Turner S, Neas B, Mathian A, Koss MN, Stohl W, et al. (2009). Deficiency of type I IFN receptor in lupus-prone New Zealand mixed 2328 mice decreases dendritic cell numbers and activation and protects from disease. J Immunol 183, 6021–6029. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Mayouf SM, Sunker A, Abdwani R, Abrawi SA, Almurshedi F, Alhashmi N, Al Sonbul A, Sewairi W, Qari A, Abdallah E, et al. (2011). Loss-of-function variant in DNASE1L3 causes a familial form of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 43, 1186–1188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

