Antibody RING-Mediated Destruction of Endogenous Proteins
- PMID: 32454028
- PMCID: PMC7332993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.032
Antibody RING-Mediated Destruction of Endogenous Proteins
Abstract
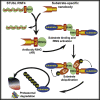
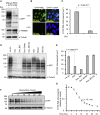
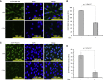
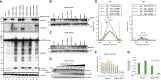
To understand gene function, the encoding DNA or mRNA transcript can be manipulated and the consequences observed. However, these approaches do not have a direct effect on the protein product of the gene, which is either permanently abrogated or depleted at a rate defined by the half-life of the protein. We therefore developed a single-component system that could induce the rapid degradation of the specific endogenous protein itself. A construct combining the RING domain of ubiquitin E3 ligase RNF4 with a protein-specific camelid nanobody mediates target destruction by the ubiquitin proteasome system, a process we describe as antibody RING-mediated destruction (ARMeD). The technique is highly specific because we observed no off-target protein destruction. Furthermore, bacterially produced nanobody-RING fusion proteins electroporated into cells induce degradation of target within minutes. With increasing availability of protein-specific nanobodies, this method will allow rapid and specific degradation of a wide range of endogenous proteins.
Keywords: ARMeD; E3 ligase; nanobody-RING fusion; proteasome; protein degradation; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bailly A.P., Perrin A., Serrano-Macia M., Maghames C., Leidecker O., Trauchessec H., Martinez-Chantar M.L., Gartner A., Xirodimas D.P. The Balance between Mono- and NEDD8-Chains Controlled by NEDP1 upon DNA Damage Is a Regulatory Module of the HSP70 ATPase Activity. Cell Rep. 2019;29:212–224.e8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caussinus E., Kanca O., Affolter M. Fluorescent fusion protein knockout mediated by anti-GFP nanobody. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011;19:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Chirichella M., Lisi S., Fantini M., Goracci M., Calvello M., Brandi R., Arisi I., D’Onofrio M., Di Primio C., Cattaneo A. Post-translational selective intracellular silencing of acetylated proteins with de novo selected intrabodies. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:279–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

