Organ-Protective Effects and the Underlying Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine
- PMID: 32454792
- PMCID: PMC7232715
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6136105
Organ-Protective Effects and the Underlying Mechanism of Dexmedetomidine
Abstract
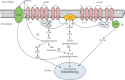
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is a highly selective α2 adrenergic receptor (α2AR) agonist currently used in clinical settings. Because DEX has dose-dependent advantages of sedation, analgesia, antianxiety, inhibition of sympathetic nervous system activity, cardiovascular stabilization, and significant reduction of postoperative delirium and agitation, but does not produce respiratory depression and agitation, it is widely used in clinical anesthesia and ICU departments. In recent years, much clinical study and basic research has confirmed that DEX has a protective effect on a variety of organs, including the nervous system, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, and small intestine. It acts by reducing the inflammatory response in these organs, activating antiapoptotic signaling pathways which protect cells from damage. Therefore, based on wide clinical application and safety, DEX may become a promising clinical multiorgan protection drug in the future. In this article, we review the physiological effects related to organ protection in α2AR agonists along with the organ-protective effects and mechanisms of DEX to understand their combined application value.
Copyright © 2020 Naren Bao and Bing Tang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

