Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids of Belladine-Type from Narcissus pseudonarcissus cv. Carlton as New Selective Inhibitors of Butyrylcholinesterase
- PMID: 32455879
- PMCID: PMC7277649
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10050800
Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids of Belladine-Type from Narcissus pseudonarcissus cv. Carlton as New Selective Inhibitors of Butyrylcholinesterase
Abstract
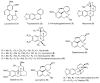
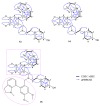
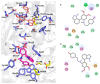
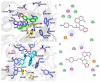
Thirteen known (1-12 and 16) and three previously undescribed Amaryllidaceae alkaloids of belladine structural type, named carltonine A-C (13-15), were isolated from bulbs of Narcissus pseudonarcissus cv. Carlton (Amaryllidaceae) by standard chromatographic methods. Compounds isolated in sufficient amounts, and not tested previously, were evaluated for their in vitro acetylcholinesterase (AChE; E.C. 3.1.1.7), butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE; E.C. 3.1.1.8) and prolyl oligopeptidase (POP; E.C. 3.4.21.26) inhibition activities. Significant human BuChE (hBUChE) inhibitory activity was demonstrated by newly described alkaloids carltonine A (13) and carltonine B (14) with IC50 values of 913 ± 20 nM and 31 ± 1 nM, respectively. Both compounds displayed a selective inhibition pattern for hBuChE with an outstanding selectivity profile over AChE inhibition, higher than 100. The in vitro data were further supported by in silico studies of the active alkaloids 13 and 14 in the active site of hBuChE.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amaryllidaceae; Narcissus pseudonarcissus cv. Carlton; alkaloids; butyrylcholinesterase; carltonine A–C; docking studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent Progress on Biological Activity of Amaryllidaceae and Further Isoquinoline Alkaloids in Connection with Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2021 Aug 29;26(17):5240. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175240. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amaryllidaceae alkaloids from Narcissus pseudonarcissus L. cv. Dutch Master as potential drugs in treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Phytochemistry. 2019 Sep;165:112055. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.112055. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Phytochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31261031
-
Alkaloids of Zephyranthes citrina (Amaryllidaceae) and their implication to Alzheimer's disease: Isolation, structural elucidation and biological activity.Bioorg Chem. 2021 Feb;107:104567. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104567. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33387730
-
Structure Elucidation and Cholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Two New Minor Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids.Molecules. 2021 Feb 26;26(5):1279. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051279. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33652925 Free PMC article.
-
Advances on the Amaryllidacea Alkaloids Collected in South Africa, Andean South America and the Mediterranean Basin.Molecules. 2023 May 12;28(10):4055. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104055. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Progress on Biological Activity of Amaryllidaceae and Further Isoquinoline Alkaloids in Connection with Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2021 Aug 29;26(17):5240. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175240. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and Biological Activities of Newly Discovered Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids.Molecules. 2020 Oct 23;25(21):4901. doi: 10.3390/molecules25214901. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33113950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids from Clivia miniata (Lindl.) Bosse (Amaryllidaceae): Isolation, Structural Elucidation, and Biological Activity.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;11(22):3034. doi: 10.3390/plants11223034. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432763 Free PMC article.
-
Semisynthetic Derivatives of Selected Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids as a New Class of Antimycobacterial Agents.Molecules. 2021 Oct 4;26(19):6023. doi: 10.3390/molecules26196023. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34641567 Free PMC article.
-
Laccase-Catalyzed 1,4-Dioxane-Mediated Synthesis of Belladine N-Oxides with Anti-Influenza A Virus Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 29;22(3):1337. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031337. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nichols E., Szoeke C.E.I., Vollset S.E., Abbasi N., Abd-Allah F., Abdela J., Aichour M.T.E., Akinyemi R.O., Alahdab F., Asgedom S.W., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:88–106. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30403-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hampel H., Mesulam M.-M., Cuello A.C., Farlow M.R., Giacobini E., Grossberg G.T., Khachaturian A.S., Vergallo A., Cavedo E., Snyder P.J., et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2018;141:1917–1933. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GA UK Nr. 178518, SVV UK 260 412, 260 401; Progres/UK Q40 and Q42/Univerzita Karlova v Praze/International
- Nr. 00179906/University Hospital Hradec Kralove/International
- Czech Science Foundation (project Nr. 20-29633J/Czech Science Foundation/International
- Long-term development plan/Faculty of Military Health Sciences/International
- Nr. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000841/European Union (EFSA-CDN)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

