Neuroprotective Effects of Euonymus alatus Extract on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits in Mice
- PMID: 32456069
- PMCID: PMC7278771
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9050449
Neuroprotective Effects of Euonymus alatus Extract on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits in Mice
Abstract
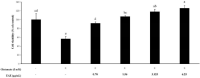
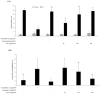
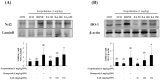
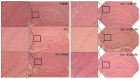
Euonymus alatus is considered to elicit various beneficial effects against cancer, hyperglycemia, menstrual discomfort, diabetic complications, and detoxification. The young leaves of this plant are exploited as food and also utilized for traditional medicine in East Asian countries, including Korea and China. Our preliminary study demonstrated that ethanolic extract from the Euonymus alatus leaf (EAE) exhibited the strongest antioxidant enzyme-inducing activity among more than 100 kinds of edible tree leaf extracts. This study investigated whether EAE could attenuate the cognitive deficits caused by oxidative stress in mice. Oral intubation of EAE at 100 mg/kg bw or higher resulted in significant improvements to the memory and behavioral impairment induced via i.p. injection of scopolamine. Furthermore, EAE enhanced the expression levels of hippocampal neurotrophic factors such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor in mice, activated the Nrf2, and the downstream heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) a quintessential antioxidant enzyme. As rutin (quercetin-3-O-rutinose) was abundantly present in EAE and free quercetin was able to induce defensive antioxidant enzymes in an Nrf2-dependent manner, our findings suggested that quercetin derived from rutin via the intestinal microflora played a significant role in the protection of the mouse hippocampus from scopolamine-induced damage through BDNF-mediated Nrf2 activation, thereby dampening cognitive decline.
Keywords: BDNF; Euonymus alatus; HT22 cells; animal model; antioxidant; cognition improvement; neuroprotective.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Bahn G., Park J.S., Yun U.J., Lee Y.J., Choi Y., Park J.S., Baek S.H., Choi B.Y., Cho Y.S., Kim H.K., et al. NRF2/ARE pathway negatively regulates BACE1 expression and ameliorates cognitive deficits in mouse Alzheimer’s models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:12516–12523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819541116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lipton S.A., Rezaie T., Nutter A., Lopez K.M., Parker J., Kosaka K., Satoh T., McKercher S.R., Masliah E., Nakanishi N. Therapeutic advantage of pro-electrophilic drugs to activate the Nrf2/ARE pathway in Alzheimer’s disease models. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7:e2499. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

