Esophageal Manometry
- PMID: 32457170
- PMCID: PMC7362579
- DOI: 10.4187/respcare.07425
Esophageal Manometry
Abstract
The estimation of pleural pressure with esophageal manometry has been used for decades, and it has been a fertile area of physiology research in healthy subject as well as during mechanical ventilation in patients with lung injury. However, its scarce adoption in clinical practice takes its roots from the (false) ideas that it requires expertise with years of training, that the values obtained are not reliable due to technical challenges or discrepant methods of calculation, and that measurement of esophageal pressure has not proved to benefit patient outcomes. Despites these criticisms, esophageal manometry could contribute to better monitoring, optimization, and personalization of mechanical ventilation from the acute initial phase to the weaning period. This review aims to provide a comprehensive but comprehensible guide addressing the technical aspects of esophageal catheter use, its application in different clinical situations and conditions, and an update on the state of the art with recent studies on this topic and on remaining questions and ways for improvement.
Keywords: ARDS; asynchrony; mechanical ventilation; mechanical ventilator weaning; physiologic monitoring; respiratory mechanics.
Copyright © 2020 by Daedalus Enterprises.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Pham has disclosed a relationship with BetterCare. Dr Telias has disclosed relationships with the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Covidien, and MbMed SA. Dr Beitler has disclosed no conflicts of interest.
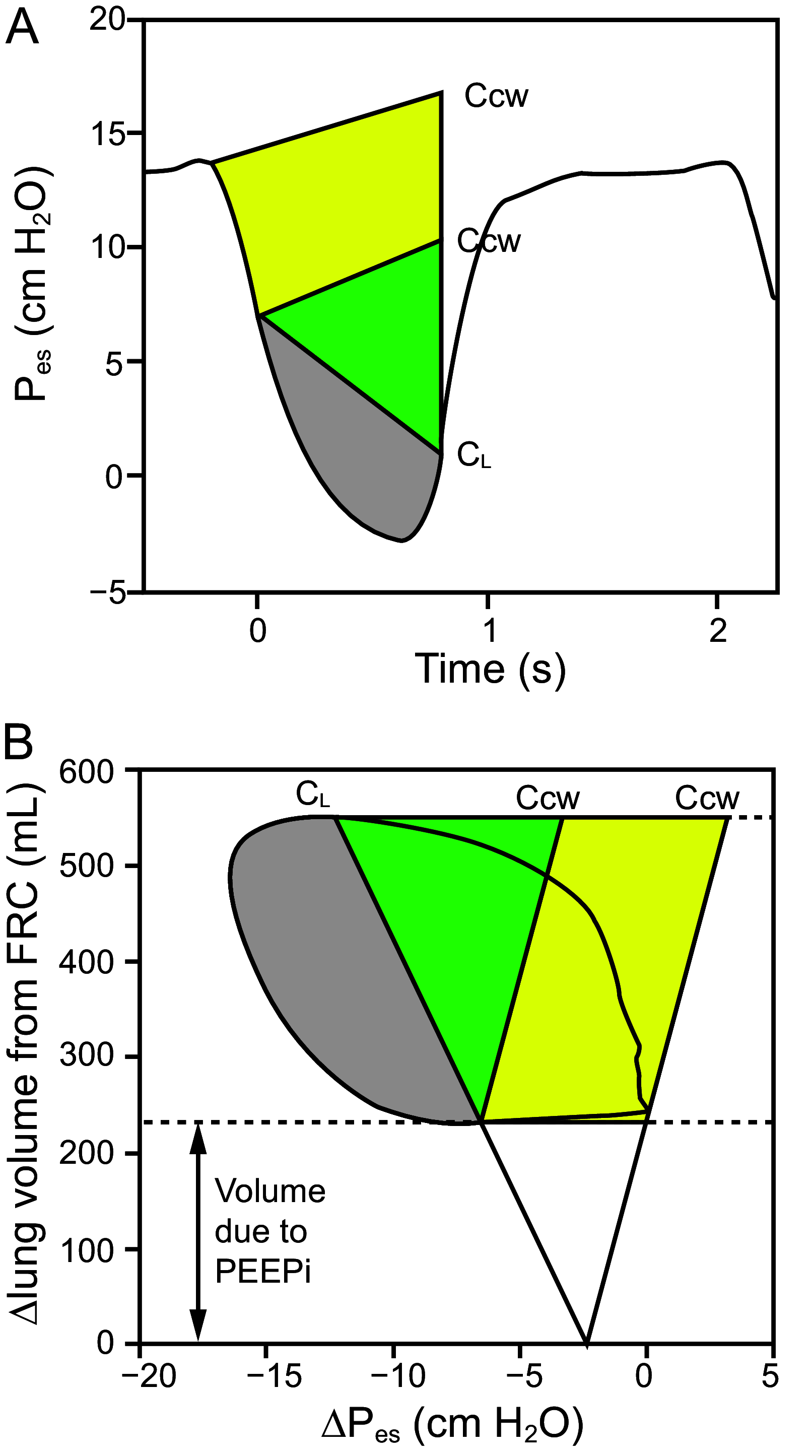
Figures


References
-
- Luciani L. Esame comparativo dei metodi per registrare la pressione toracica e addominale. In: Delle oscillazioni della pressione intratoracica e intraddominale. Torino, Italy: Vicenzo Bona; 1877:2-18.
-
- Buytendijk HJ. Oesophagusdruk en longelasticiteit. Dissertation, University of Groningen 1949.
-
- Mead J, McIlroy MB, Selverstone NJ, Kriete BC. Measurement of intraesophageal pressure. J Appl Physiol 1955;7(5):491-495. - PubMed
-
- Mead J, Gaensler EA. Esophageal and pleural pressures in man, upright and supine. J Appl Physiol 1959;14(1):81-83. - PubMed
-
- Milic-Emili G, Petit JM. Relationship between endoesophageal and intrathoracic pressure variations in dog. J Appl Physiol 1959;14(4):535-537.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

