The UK Biobank imaging enhancement of 100,000 participants: rationale, data collection, management and future directions
- PMID: 32457287
- PMCID: PMC7250878
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-15948-9
The UK Biobank imaging enhancement of 100,000 participants: rationale, data collection, management and future directions
Abstract
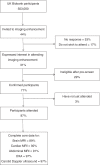
UK Biobank is a population-based cohort of half a million participants aged 40-69 years recruited between 2006 and 2010. In 2014, UK Biobank started the world's largest multi-modal imaging study, with the aim of re-inviting 100,000 participants to undergo brain, cardiac and abdominal magnetic resonance imaging, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and carotid ultrasound. The combination of large-scale multi-modal imaging with extensive phenotypic and genetic data offers an unprecedented resource for scientists to conduct health-related research. This article provides an in-depth overview of the imaging enhancement, including the data collected, how it is managed and processed, and future directions.
Conflict of interest statement
Nicholas C. Harvey acknowledges consultancy/grant support/honoraria from Alliance for Better Bone Health, AMGEN, UCB, Radius Health, MSD, Eli Lilly, Servier, Shire, Consilient Healthcare and Internis Pharma, outside the submitted work. Paul Leeson acknowledges grant support from Lantheus Medical Imaging and Fukuda, consultancy fees from Intelligent Ultrasound and is a non-executive director of Ultromics. Steffen E. Petersen acknowledges consultancy fees from Circle Cardiovascular Imaging Inc., Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Paul Matthews acknowledges consultancy fees from Roche, Adelphi Communications, Celgene and Biogen. He has received honoraria or speakers’ honoraria from Novartis, Biogen and Roche and has received research or educational funds from Biogen, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline and Nodthera. He is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board to the Board of Ipsen Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/N026934/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17114/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 107190/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/11/65/28865/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 202788/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- PG/17/13/32860/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G9901399/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9409531/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900897/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G9409634/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15067/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K501013/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources