Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 32457361
- PMCID: PMC7251120
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16439-7
Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophage-biomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines
Abstract
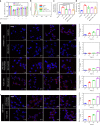
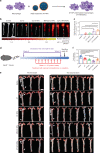
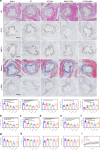
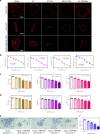
Vascular disease remains the leading cause of death and disability, the etiology of which often involves atherosclerosis. The current treatment of atherosclerosis by pharmacotherapy has limited therapeutic efficacy. Here we report a biomimetic drug delivery system derived from macrophage membrane coated ROS-responsive nanoparticles (NPs). The macrophage membrane not only avoids the clearance of NPs from the reticuloendothelial system, but also leads NPs to the inflammatory tissues, where the ROS-responsiveness of NPs enables specific payload release. Moreover, the macrophage membrane sequesters proinflammatory cytokines to suppress local inflammation. The synergistic effects of pharmacotherapy and inflammatory cytokines sequestration from such a biomimetic drug delivery system lead to improved therapeutic efficacy in atherosclerosis. Comparison to macrophage internalized with ROS-responsive NPs, as a live-cell based drug delivery system for treatment of atherosclerosis, suggests that cell membrane coated drug delivery approach is likely more suitable for dealing with an inflammatory disease than the live-cell approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Macrophage mimetics to target atherosclerosis.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020 Aug;17(8):454. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-0404-x. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32528187 No abstract available.
References
-
- Allahverdian S, Chehroudi AC, McManus BM, Abraham T, Francis GA. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2014;129:1551–1559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

