Key role of the 5-HT1A receptor addressing protein Yif1B in serotonin neurotransmission and SSRI treatment
- PMID: 32459080
- PMCID: PMC7850149
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.190134
Key role of the 5-HT1A receptor addressing protein Yif1B in serotonin neurotransmission and SSRI treatment
Abstract
Background: Altered function of serotonin receptor 1A (5-HT1AR) has been consistently implicated in anxiety, major depressive disorder and resistance to antidepressants. Mechanisms by which the function of 5-HT1AR (expressed as an autoreceptor in serotonergic raphe neurons and as a heteroreceptor in serotonin [5-HT] projection areas) is altered include regulation of its expression, but 5-HT1AR trafficking may also be involved.
Methods: We investigated the consequences of the lack of Yif1B (the 5-HT1AR trafficking protein) on 5-HT neurotransmission in mice, and whether Yif1B expression might be affected under conditions known to alter 5-HT neurotransmission, such as anxious or depressive states or following treatment with fluoxetine (a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) in humans, monkeys and mice.
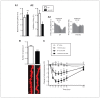
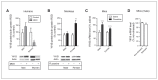
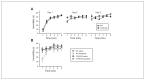
Results: Compared with wild-type mice, Yif1B-knockout mice showed a significant decrease in the forebrain density of 5-HT projection fibres and a hypofunctionality of 5-HT1A autoreceptors expressed on raphe 5-HT neurons. In addition, social interaction was less in Yif1B-knockout mice, which did not respond to the antidepressant-like effect of acute fluoxetine injection. In wild-type mice, social defeat was associated with downregulated Yif1B mRNA in the prefrontal cortex, and chronic fluoxetine treatment increased Yif1B expression. The expression of Yif1B was also downregulated in the postmortem prefrontal cortex of people with major depressive disorder and upregulated after chronic treatment with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in monkeys.
Limitations: We found sex differences in Yif1B expression in humans and monkeys, but not in mice under the tested conditions.
Conclusion: These data support the concept that Yif1B plays a critical role in 5-HT1AR functioning and brain 5-HT homeostasis. The opposite changes in its expression observed in anxious or depressive states and after therapeutic fluoxetine treatment suggest that Yif1B might be involved in vulnerability to anxiety and depression, and fluoxetine efficacy.
© 2020 Joule Inc. or its licensors.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Loss of Adult 5-HT1A Autoreceptors Results in a Paradoxical Anxiogenic Response to Antidepressant Treatment.J Neurosci. 2019 Feb 20;39(8):1334-1346. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0352-18.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 14. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30552180 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid reorganization of serotonin projections and antidepressant response to 5-HT1A-biased agonist NLX-101 in fluoxetine-resistant cF1ko mice.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Dec 15;261:110132. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110132. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39208980
-
Acute 5-HT₁A autoreceptor knockdown increases antidepressant responses and serotonin release in stressful conditions.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013 Jan;225(1):61-74. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2795-9. Epub 2012 Jul 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013. PMID: 22820867
-
Pharmacology of rapid-onset antidepressant treatment strategies.J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62 Suppl 15:12-7. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11444761 Review.
-
Effects of the antidepressant fluoxetine on the subcellular localization of 5-HT1A receptors and SERT.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Sep 5;367(1601):2416-25. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0361. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22826342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HTR1A Gene Polymorphism in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Comorbid with Major Depressive Disorder in a Chinese Population.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 May 25;15:1597-1604. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S361843. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35651901 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral, Hormonal, and Serotonergic Responses to Different Restricted Feeding Schedules in Rats.Int J Tryptophan Res. 2022 Jun 20;15:11786469221104729. doi: 10.1177/11786469221104729. eCollection 2022. Int J Tryptophan Res. 2022. PMID: 35757086 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the eukaryotic Yip and REEP/Yop superfamily of membrane-shaping adapter proteins (MSAPs): A cacophony or harmony of structure and function?Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Aug 19;9:912848. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.912848. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36060263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pham TH, Mendez-David I, Defaix C, et al. Ketamine treatment involves medial prefrontal cortex serotonin to induce a rapid antidepressant-like activity in BALB/cJ mice. Neuropharmacology. 2017;112:198–209. - PubMed
-
- Hamani C, Diwan M, Macedo CE, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of medial prefrontal cortex deep brain stimulation in rats. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:117–24. - PubMed
-
- Masson J, Emerit MB, Hamon M, et al. Serotonergic signaling: multiple effectors and pleiotropic effects. WIREs Membr Transp Signal. 2012;1:685–713.
-
- Le Poul E, Laaris N, Doucet E, et al. Early desensitization of somato-dendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors in rats treated with fluoxetine or paroxetine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995;352:141–8. - PubMed
-
- Lanzenberger RR, Mitterhauser M, Spindelegger C, et al. Reduced serotonin-1A receptor binding in social anxiety disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:1081–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
