COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) - Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?
- PMID: 32459372
- PMCID: PMC7283873
- DOI: 10.1111/joim.13101
COVID-19 and renin-angiotensin system inhibition: role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) - Is there any scientific evidence for controversy?
Abstract
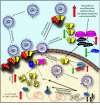
Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockers are extensively used worldwide to treat many cardiovascular disorders, where they are effective in reducing both mortality and morbidity. These drugs are known to induce an increased expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). ACE2 acts as receptor for the novel SARS coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) which raising the important issue of possible detrimental effects that RAS blockers could exert on the natural history and pathogenesis of the coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) and associated excessive inflammation, myocarditis and cardiac arrhythmias. We review the current knowledge on the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 infection and RAS blockers and suggest a scientific rationale for continuing RAS blockers therapy in patients with COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: ACEIs/ARBs; COVID-19; RAAS; SARS coronavirus (CoV)-2; angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2); cardiovascular system; pandemic.
© 2020 The Association for the Publication of the Journal of Internal Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
A potential link between RAAS, obesity and atrial fibrillation in COVID-19 infection.J Intern Med. 2021 Apr;289(4):588. doi: 10.1111/joim.13186. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33140481 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . A research and development Blueprint for action to prevent epidemics. 2020. https://www.who.int/blueprint/en/.
-
- WHO . Coronavirus. 2020. https://www.who.int/health‐topics/coronavirus#tab=tab_1.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

