Long term outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma without macrovascular invasion
- PMID: 32460180
- PMCID: PMC7340168
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.04.024
Long term outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma without macrovascular invasion
Abstract
Background: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) is a non-invasive ablative treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This report aimed to address the limited availability of long-term outcomes after SBRT for HCC from North America.
Methods: Localized HCC patients without vascular invasion, who were ineligible for other liver-directed therapies and treated with SBRT at the University of Toronto or University of Michigan, were pooled to determine overall survival (OS), cumulative recurrence rates, and ≥ grade-3 toxicity. Multivariable analysis determined factors affecting OS and local recurrence rates.
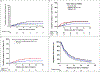
Results: In 297 patients with 436 HCCs (42% > 3 cm), one-, three- and five-year OS was 77·3%, 39·0% and 24·1%, respectively. On Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, liver transplant after SBRT, Child-Pugh A liver function, alpha-fetoprotein ≤ 10 ng/ml, and Eastern Co-operative Oncology Group performance status 0 significantly improved OS (hazard ratio [HR] = 0·06, 95% confidence interval [CI- 0·02-0·25; p<0·001; HR = 0·42, 95% CI = 0·29-0·60, p<0·001; HR = 0·61, 95% CI- 0·44-0·83; p=0·002 and HR = 0·71, 95% CI = 0·51-0·97, p=0·034, respectively). Cumulative local recurrence was 6·3% (95% CI = 0.03-0.09) and 13·3% (95% CI = 0.06-0.21) at one and three years, respectively. Using Cox regression modelling, local control was significantly higher using breath-hold motion management and in HCC smaller than 3 cm (HR = 0.52, 95% CI = 0.58-0.98; p=0.042 and HR = 0.53, 95% CI = 0.26-0.98; p=0.042, respectively). Worsening of Child-Pugh score by ≥2 points three months after SBRT was seen in 15.9%.
Conclusions: SBRT confers high local control and long-term survival in a substantial proportion of HCC patients unsuitable for, or refractory to standard loco-regional treatments. Liver transplant should be considered if appropriate downsizing occurs after SBRT.
Keywords: Cancer; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver; Radiation; Stereotactic.
Crown Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement L.A.D has a licencing agreement for Raysearch image registration software (unrelated). A.B. has a consulting/advisory role with Astra Zeneca. K.C. received research funding from BTG and Varian Medical Systems. M.F. has a consulting/advisory role in GenomeDx, Myriad Pharmaceuticals, NanoString Technologies and Varian Medical Systems. She receives honoraria from Medivation/Astellas (also in Speaker's bureau); Myriad Pharmaceuticals; Reflexion Medical and research funding from Celgene (I); Varian Medical Systems (Inst). She also received travel expenses from GenomeDx and has a pending patent for RadioType Dx, a biomarker test. A.S.M, E.A., D.O., R.D., J.K., J.R., R.W., C.M., J.B., C.C. and T.S.L. had no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer: EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2012;56:908–943 - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Fuster J, Bruix J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: resection versus transplantation. Hepatology. 1999. December;30(6):1434ª–40. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Real MI, Montana X, et al. Arterial embolization or chemoembolization versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2002; 359: 1734–1739. - PubMed
-
- Ball D, Mai GT, Vinod S, et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard radiotherapy in stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer (TROG 09.02 CHISEL): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; pii: S1470–2045(18)30896–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

