Dysphagia in COVID-19 -multilevel damage to the swallowing network?
- PMID: 32460415
- PMCID: PMC7283711
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.14367
Dysphagia in COVID-19 -multilevel damage to the swallowing network?
Keywords: COVID-19; dysphagia; fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation of swallowing; swallowing.
Conflict of interest statement
R.D. and T.W. declare no financial or other conflicts of interest. P.Z. reports (full departmental disclosure) grants from Orion Pharma, Abbott Nutrition International, B. Braun Medical AG, CSEM AG, Edwards Lifesciences Services GmbH, Kenta Biotech Ltd, Maquet Critical Care AB, Omnicare Clinical Research AG, Nestlé, Pierre Fabre Pharma AG, Pfizer, Bard Medica S.A., Abbott AG, Anandic Medical Systems, Pan Gas AG Healthcare, Bracco, Hamilton Medical AG, Fresenius Kabi, Getinge Group Maquet AG, Dräger AG, Teleflex Medical GmbH, Glaxo Smith Kline, Merck Sharp and Dohme AG, Eli Lily and Company, Baxter, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, CSL Behring, Novartis, Covidien and Nycomed outside the submitted work. J.C.S. reports (full departmental disclosure) grants from Orion Pharma, Abbott Nutrition International, B. Braun Medical AG, CSEM AG, Edwards Lifesciences Services GmbH, Kenta Biotech Ltd, Maquet Critical Care AB, Omnicare Clinical Research AG, Nestlé, Pierre Fabre Pharma AG, Pfizer, Bard Medica S.A., Abbott AG, Anandic Medical Systems, Pan Gas AG Healthcare, Bracco, Hamilton Medical AG, Fresenius Kabi, Getinge Group Maquet AG, Dräger AG, Teleflex Medical GmbH, Glaxo Smith Kline, Merck Sharp and Dohme AG, Eli Lily and Company, Baxter, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, CSL Behring, Novartis, Covidien and Nycomed outside the submitted work.
Figures
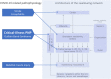
Comment on
-
COVID-19: what if the brain had a role in causing the deaths?Eur J Neurol. 2020 Sep;27(9):e41-e42. doi: 10.1111/ene.14275. Epub 2020 May 14. Eur J Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32333819 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Marian T, Dunser M, Citerio G, Kokofer A, Dziewas R. Are intensive care physicians aware of dysphagia? The MAD(ICU) survey results. Intensive Care Med 2018; 44: 973–975. - PubMed
-
- Schefold JC, Berger D, Zurcher P, et al. Dysphagia in mechanically ventilated ICU patients (DYnAMICS): a prospective observational trial. Crit Care Med 2017; 45: 2061–2069. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

