Urinary activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule as a novel biomarker of lupus nephritis histology
- PMID: 32460901
- PMCID: PMC7251704
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02209-9
Urinary activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule as a novel biomarker of lupus nephritis histology
Abstract
Background: Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most severe complications of SLE patients. We aim to validate urinary ALCAM as a biomarker in predicting renal disease histpathology in a Chinese lupus cohort.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, a total of 256 patients and controls were recruited. Urinary levels of ALCAM were determined by ELISA. Renal histopathology was reviewed by an experienced renal pathologist.
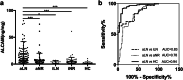
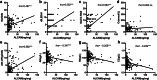
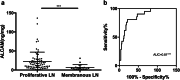
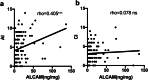
Results: Urinary ALCAM levels were significantly increased in active LN patients when compared to active SLE patients without renal involvement (p < 0.001), inactive LN patients (p = 0.023), inactive SLE patients without renal involvement (p < 0.001), and healthy controls (p < 0.001). Correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between urinary ALCAM and general disease activity-SLEDAI score (r = 0.487, p < 0.001), as well as renal disease activity-rSLEDAI (r = 0.552, p < 0.001) and SLICC RAS (r = 0.584, p < 0.001). Urinary ALCAM also correlated with lab parameters including 24-h urine protein, hemoglobin, and complement 3. Moreover, urinary ALCAM levels were significantly increased in class III and IV (proliferative) LN as compared to those in class V (membranous) LN. It outperformed conventional biomarkers (anti-dsDNA antibody, C3, C4, proteinuria) in discriminating the two groups of LN. On renal histopathology, urinary ALCAM levels correlated positively with activity index (r = 0.405, p < 0.001) but not chronicity index (r = 0.079, p = 0.448).
Conclusion: Urinary ALCAM is a potential biomarker for predicting renal pathology activity in LN and may serve as a valuable surrogate marker of renal histopathology.
Keywords: ALCAM; Activity index; Chronicity index; Lupus nephritis; Renal histopathology; Urinary biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinico-serological associations of urinary activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Mar;43(3):1015-1021. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06883-x. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38294724 Free PMC article.
-
Urine ALCAM, PF4 and VCAM-1 Surpass Conventional Metrics in Identifying Nephritis Disease Activity in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:885307. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.885307. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720325 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring urine:serum fractional excretion ratios as potential biomarkers for lupus nephritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 24;13:910993. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.910993. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091001 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic, predictive and prognostic biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus: current insights.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022 Mar 1;34(2):139-149. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000862. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35013077 Review.
-
Interferon-Inducible Protein 10 and Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4954. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194954. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel technology for home monitoring of lupus nephritis that tracks the pathogenic urine biomarker ALCAM.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 9;13:1044743. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1044743. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569940 Free PMC article.
-
Treat-to-Target in Lupus Nephritis. What is the Role of the Repeat Kidney Biopsy?Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Feb 11;70(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00646-9. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 35147824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinico-serological associations of urinary activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Mar;43(3):1015-1021. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06883-x. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38294724 Free PMC article.
-
Current Insights on Biomarkers in Lupus Nephritis: A Systematic Review of the Literature.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 28;11(19):5759. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195759. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis identifies subgroups of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Proteomics. 2023 Jul 29;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12014-023-09420-1. Clin Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37516862 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

