Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Strains 17 syn+ and KOS(M) Differ Greatly in Their Ability To Reactivate from Human Neurons In Vitro
- PMID: 32461310
- PMCID: PMC7375381
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00796-20
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Strains 17 syn+ and KOS(M) Differ Greatly in Their Ability To Reactivate from Human Neurons In Vitro
Abstract
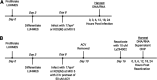
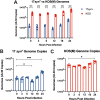
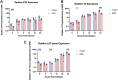
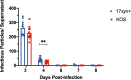
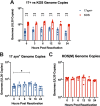
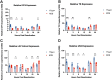
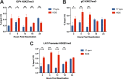
Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) establishes a lifelong latent infection in peripheral nerve ganglia. Periodically, the virus reactivates from this latent reservoir and is transported to the original site of infection. Strains of HSV-1 have been noted to vary greatly in their virulence and reactivation efficiencies in animal models. While HSV-1 strain 17syn+ can be readily reactivated, strain KOS(M) shows little to no reactivation in the mouse and rabbit models of induced reactivation. Additionally, 17syn+ is markedly more virulent in vivo than KOS. This has raised questions regarding potential strain-specific differences in neuroinvasion and neurovirulence and their contribution to differences in the establishment of latency (or ability to spread back to the periphery) and to the reactivation phenotype. To determine if any difference in the ability to reactivate between strains 17syn+ and KOS(M) is manifest at the level of neurons, we utilized a recently characterized human neuronal cell line model of HSV latency and reactivation (LUHMES). We found that KOS(M) established latency with a higher number of viral genomes than strain 17syn+ Strikingly, we show that the KOS(M) viral genomes have a higher burden of heterochromatin marks than strain 17syn+ The increased heterochromatin profile for KOS(M) correlates with the reduced expression of viral lytic transcripts during latency and impaired induced reactivation compared to that of 17syn+ These results suggest that genomes entering neurons from HSV-1 infections with strain KOS(M) are more prone to rapid heterochromatinization than those of 17syn+ and that this results in a reduced ability to reactivate from latency.IMPORTANCE Herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) establishes a lifelong infection in neuronal cells. The virus periodically reactivates and causes recurrent disease. Strains of HSV-1 vary greatly in their virulence and potential to reactivate in animal models. Although these differences are phenotypically well defined, factors contributing to the strains' abilities to reactivate are largely unknown. We utilized a human neuronal cell line model of HSV latency and reactivation (LUHMES) to characterize the latent infection of two HSV-1 wild-type strains. We find that strain-specific differences in reactivation are recapitulated in LUHMES. Additionally, these differences correlate with the degree of heterochromatinization of the latent genomes. Our data suggest that the epigenetic state of the viral genome is an important determinant of reactivation that varies in a strain-specific manner. This work also shows the first evidence of strain-specific differences in reactivation outside the context of the whole animal at a human neuronal cell level.
Keywords: herpes simplex virus; latency; neurotropism; neurovirulence; reactivation.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Hill JM, Garza HH Jr, Su YH, Meegalla R, Hanna LA, Loutsch JM, Thompson HW, Varnell ED, Bloom DC, Block TM. 1997. A 437-base-pair deletion at the beginning of the latency-associated transcript promoter significantly reduced adrenergically induced herpes simplex virus type 1 ocular reactivation in latently infected rabbits. J Virol 71:6555–6559. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.9.6555-6559.1997. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hill JM, Maggioncalda JB, Garza HH Jr, Su YH, Fraser NW, Block TM. 1996. In vivo epinephrine reactivation of ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 in the rabbit is correlated to a 370-base-pair region located between the promoter and the 5’ end of the 2.0 kilobase latency-associated transcript. J Virol 70:7270–7274. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.10.7270-7274.1996. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

