Functional role of kallikrein 5 and proteinase-activated receptor 2 in eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 32461336
- PMCID: PMC7350155
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz7773
Functional role of kallikrein 5 and proteinase-activated receptor 2 in eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
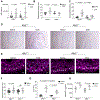
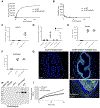
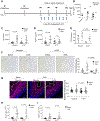
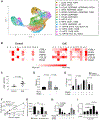
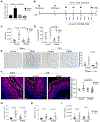
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, food antigen-driven, inflammatory disease of the esophagus and is associated with impaired barrier function. Evidence is emerging that loss of esophageal expression of the serine peptidase inhibitor, kazal type 7 (SPINK7), is an upstream event in EoE pathogenesis. Here, we provide evidence that loss of SPINK7 mediates its pro-EoE effects via kallikrein 5 (KLK5) and its substrate, protease-activated receptor 2 (PAR2). Overexpression of KLK5 in differentiated esophageal epithelial cells recapitulated the effect of SPINK7 gene silencing, including barrier impairment and loss of desmoglein-1 expression. Conversely, KLK5 deficiency attenuated allergen-induced esophageal protease activity, modified commensal microbiome composition, and attenuated eosinophilia in a murine model of EoE. Inhibition of PAR2 blunted the cytokine production associated with loss of SPINK7 in epithelial cells and attenuated the allergen-induced esophageal eosinophilia in vivo. Clinical samples substantiated dysregulated PAR2 expression in the esophagus of patients with EoE, and delivery of the clinically approved drug α1 antitrypsin (A1AT, a protease inhibitor) inhibited experimental EoE. These findings demonstrate a role for the balance between KLK5 and protease inhibitors in the esophagus and highlight EoE as a protease-mediated disease. We suggest that antagonizing KLK5 and/or PAR2 has potential to be therapeutic for EoE.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


References
-
- Dellon ES, Liacouras CA, Molina-Infante J, Furuta GT, Spergel JM, Zevit N, Spechler SJ, Attwood SE, Straumann A, Aceves SS, Alexander JA, Atkins D, Arva NC, Blanchard C, Bonis PA, Book WM, Capocelli KE, Chehade M, Cheng E, Collins MH, Davis CM, Dias JA, Di Lorenzo C, Dohil R, Dupont C, Falk GW, Ferreira CT, Fox A, Gonsalves NP, Gupta SK, Katzka DA, Kinoshita Y, Menard-Katcher C, Kodroff E, Metz DC, Miehlke S, Muir AB, Mukkada VA, Murch S, Nurko S, Ohtsuka Y, Orel R, Papadopoulou A, Peterson KA, Philpott H, Putnam PE, Richter JE, Rosen R, Rothenberg ME, Schoepfer A, Scott MM, Shah N, Sheikh J, Souza RF, Strobel MJ, Talley NJ, Vaezi MF, Vandenplas Y, Vieira MC, Walker MM, Wechsler JB, Wershil BK, Wen T, Yang GY, Hirano I, Bredenoord AJ, Updated international consensus diagnostic criteria for eosinophilic esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE conference. Gastroenterology 155, 1022–1033.e10 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Molina-Infante J, Gonzalez-Cordero PL, Arias A, Lucendo AJ, Update on dietary therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 11, 115–123 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Rochman M, Travers J, Miracle CE, Bedard MC, Wen T, Azouz NP, Caldwell JM, Kc K, Sherrill JD, Davis BP, Rymer JK, Kaufman KM, Aronow BJ, Rothenberg ME, Profound loss of esophageal tissue differentiation in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 140, 738–749.e3 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

