Evaluating drug targets through human loss-of-function genetic variation
- PMID: 32461653
- PMCID: PMC7272226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2267-z
Evaluating drug targets through human loss-of-function genetic variation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Evaluating drug targets through human loss-of-function genetic variation.Nature. 2021 Feb;590(7846):E56. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03177-5. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33536628 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
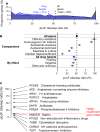
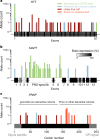
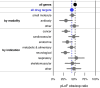
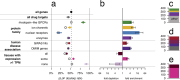
Naturally occurring human genetic variants that are predicted to inactivate protein-coding genes provide an in vivo model of human gene inactivation that complements knockout studies in cells and model organisms. Here we report three key findings regarding the assessment of candidate drug targets using human loss-of-function variants. First, even essential genes, in which loss-of-function variants are not tolerated, can be highly successful as targets of inhibitory drugs. Second, in most genes, loss-of-function variants are sufficiently rare that genotype-based ascertainment of homozygous or compound heterozygous 'knockout' humans will await sample sizes that are approximately 1,000 times those presently available, unless recruitment focuses on consanguineous individuals. Third, automated variant annotation and filtering are powerful, but manual curation remains crucial for removing artefacts, and is a prerequisite for recall-by-genotype efforts. Our results provide a roadmap for human knockout studies and should guide the interpretation of loss-of-function variants in drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
E.V.M. has received research support in the form of charitable contributions from Charles River Laboratories and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, and has consulted for Deerfield Management. K.J.K. is a shareholder of Personalis. H.C.M., B.B.C., M.W., D.R. and J.A. have no competing interests to declare. R.C.T. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of Ipsen Ltd and has current funding from the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research UK. D.A.v.H. is a shareholder of Nexpep Pty Ltd; has current or recent research funding from Wellcome Trust, Medical Research Council UK, National Institute for Health Research UK, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals; and serves on the Population & Systems Medicine Board of the Medical Research Council UK. MJD is a founder of Maze Therapeutics. S.L.S. serves on the Board of Directors of the Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation (‘GNF’); is a shareholder and serves on the Board of Directors of Jnana Therapeutics; is a shareholder of Forma Therapeutics; is a shareholder and advises Decibel Therapeutics and Eikonizo Therapeutics; serves on the Scientific Advisory Boards of Eisai Co., Ltd., Ono Pharma Foundation, Exo Therapeutics, and F-Prime Capital Partners; and is a Novartis Faculty Scholar. D.G.M. is a founder with equity in Goldfinch Bio, and has received research support from AbbVie, Astellas, Biogen, BioMarin, Eisai, Merck, Pfizer, and Sanofi-Genzyme.
Figures

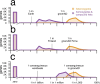
Comment in
-
Thousands of human sequences provide deep insight into single genomes.Nature. 2020 May;581(7809):385-386. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01485-4. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32461645 No abstract available.
-
Exploring human genomic diversity with gnomAD.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Aug;21(8):448. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0255-7. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32488197 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

