The effect of LRRK2 loss-of-function variants in humans
- PMID: 32461697
- PMCID: PMC7303015
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0893-5
The effect of LRRK2 loss-of-function variants in humans
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The effect of LRRK2 loss-of-function variants in humans.Nat Med. 2021 Feb;27(2):355. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-01185-6. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 33483629 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
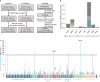
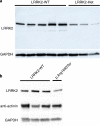
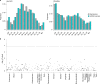
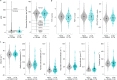
Human genetic variants predicted to cause loss-of-function of protein-coding genes (pLoF variants) provide natural in vivo models of human gene inactivation and can be valuable indicators of gene function and the potential toxicity of therapeutic inhibitors targeting these genes1,2. Gain-of-kinase-function variants in LRRK2 are known to significantly increase the risk of Parkinson's disease3,4, suggesting that inhibition of LRRK2 kinase activity is a promising therapeutic strategy. While preclinical studies in model organisms have raised some on-target toxicity concerns5-8, the biological consequences of LRRK2 inhibition have not been well characterized in humans. Here, we systematically analyze pLoF variants in LRRK2 observed across 141,456 individuals sequenced in the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD)9, 49,960 exome-sequenced individuals from the UK Biobank and over 4 million participants in the 23andMe genotyped dataset. After stringent variant curation, we identify 1,455 individuals with high-confidence pLoF variants in LRRK2. Experimental validation of three variants, combined with previous work10, confirmed reduced protein levels in 82.5% of our cohort. We show that heterozygous pLoF variants in LRRK2 reduce LRRK2 protein levels but that these are not strongly associated with any specific phenotype or disease state. Our results demonstrate the value of large-scale genomic databases and phenotyping of human loss-of-function carriers for target validation in drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
A.K., B.A., A.G., P.M., P.C. and members of the 23andMe Research Team are current or former employees of 23andMe, Inc. and hold stock or stock options in 23andMe. D.G.M. is a founder with equity in Goldfinch Bio and has received research support from AbbVie, Astellas, Biogen, BioMarin, Eisai, Merck, Pfizer and Sanofi-Genzyme. E.V.M. has received research support in the form of charitable contributions from Charles River Laboratories and Ionis Pharmaceuticals and has consulted for Deerfield Management. K.J.K. owns stock in Personalis. M.J.D. is a founder of Maze Therapeutics.
Figures
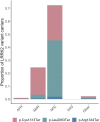
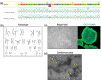

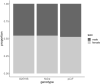

Comment in
-
Exploring human genomic diversity with gnomAD.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Aug;21(8):448. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0255-7. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32488197 No abstract available.
-
LRRK2 Loss-of-Function Variants: When Less Is More.Mov Disord. 2020 Oct;35(10):1754. doi: 10.1002/mds.28291. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Mov Disord. 2020. PMID: 32970868 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nelson MR, et al. The support of human genetic evidence for approved drug indications. Nat. Genet. 2015;47:856–860. - PubMed
-
- Plenge RM, Scolnick EM, Altshuler D. Validating therapeutic targets through human genetics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013;12:581–594. - PubMed
-
- Greggio E, et al. Kinase activity is required for the toxic effects of mutant LRRK2/dardarin. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006;23:329–341. - PubMed
-
- Andersen MA, et al. PFE-360-induced LRRK2 inhibition induces reversible, non-adverse renal changes in rats. Toxicology. 2018;395:15–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH104964/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 107469/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_1102/20/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH085548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH123451/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK105566/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 GM104371/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CS/14/2/30841/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- RG/18/10/33842/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- F32 GM115208/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

