Posible involvement of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant effects of citicoline on pentylenetetrazole and electroshock induced seizures in mice
- PMID: 32462085
- PMCID: PMC7240119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03932
Posible involvement of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant effects of citicoline on pentylenetetrazole and electroshock induced seizures in mice
Abstract
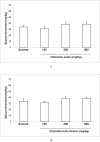
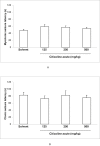
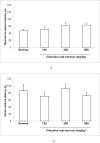
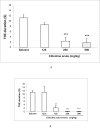
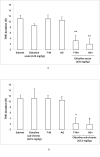
Cerebroneurovascular trauma is recognized as an important risk factor in the development of seizure and epilepsy. Administration of citicoline in these situations is a conventional therapeutic strategy, which combines neurovascular protection and repair effects. The aim of the present study is clarifying the effect of acute and sub-chronic citicoline administration on pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) and electroshock induced seizures in mice. Besides we examined the probable role of NO and its interaction with citicoline in seizure experiments. Male mice were received acute and sub-chronic regimens of different doses of citicoline (62.5, 125, 250 and 500 mg/kg) before the intravenous or intraperitoneal PTZ-induced seizures or electroshock. To clarify the probable role of NO, 7-nitroindazole (7-NI) (60 mg/kg) or aminoguanidine (AG) (100 mg/kg) were injected 5 min before citicoline in separate groups. The results revealed that neither acute nor sub-chronic treatment with citicoline could affect the seizures induced by intravenous or intraperitoneal PTZ, but in electroshock model, citicoline showed anti-epileptic properties. Co-administration of citicoline and selective nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors amplified the anticonvulsant effect of citicoline. The current results indicated that citicoline has anticonvulsant effects probably through the inhibition of NO.
Keywords: Citicoline; Electroshock; Mice; Neuroscience; Nitric oxide; Pentylenetetrazole; Seizures.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute and Sub-chronic Anticonvulsant Effects of Edaravone on Seizure Induced by Pentylenetetrazole or Electroshock in Mice, Nitric Oxide Involvement.Iran J Med Sci. 2023 May;48(3):329-340. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2022.94177.2544. Iran J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37791336 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of acute aripiprazole treatment on chemically and electrically induced seizures in mice: The role of nitric oxide.Epilepsy Behav. 2015 Jul;48:35-40. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.018. Epub 2015 May 31. Epilepsy Behav. 2015. PMID: 26037847
-
The Effects of Sub-Chronic Treatment with Aripiprazole on Pentylenetetrazole- and Electroshock-Induced Seizures in Mice: The Role of Nitric Oxide.Pharmacology. 2015;95(5-6):264-70. doi: 10.1159/000381550. Epub 2015 May 22. Pharmacology. 2015. PMID: 26022738
-
The Search for New Screening Models of Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: Is Induction of Acute Seizures in Epileptic Rodents a Suitable Approach?Neurochem Res. 2017 Jul;42(7):1926-1938. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-2025-7. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Neurochem Res. 2017. PMID: 27502939 Review.
-
Nitric oxide, epileptic seizures, and action of antiepileptic drugs.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011 Nov;10(7):808-19. doi: 10.2174/187152711798072347. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21999730 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute and Sub-chronic Anticonvulsant Effects of Edaravone on Seizure Induced by Pentylenetetrazole or Electroshock in Mice, Nitric Oxide Involvement.Iran J Med Sci. 2023 May;48(3):329-340. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2022.94177.2544. Iran J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37791336 Free PMC article.
-
Anticonvulsant effects of ivermectin on pentylenetetrazole- and maximal electroshock-induced seizures in mice: the role of GABAergic system and KATP channels.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 2;8(11):e11375. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11375. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36387449 Free PMC article.
-
Citicoline: pharmacological and clinical review, 2022 update.Rev Neurol. 2022 Nov 30;75(s05):S1-S89. doi: 10.33588/rn.75s05.2022311. Rev Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36544369 Free PMC article. Review. English, Spanish.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 1/2 Postconditioning by the Ligand Pam3cys Tempers Posttraumatic Hyperexcitability, Neuroinflammation, and Microglial Response: A Potential Candidate for Posttraumatic Epilepsy.Inflammation. 2025 Jun;48(3):1206-1219. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02109-z. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39044002
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

