Effects of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 signaling pathway on proliferation, invasion, and migration of human osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 32463132
- PMCID: PMC7521293
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23362
Effects of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 signaling pathway on proliferation, invasion, and migration of human osteosarcoma cells
Abstract
Purpose: To explore the effects of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 signaling pathway on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of human osteosarcoma cells.
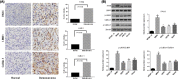
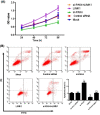
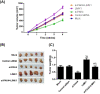
Methods: The expression of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 was detected by immunohistochemistry in osteosarcoma tissues. The osteosarcoma cell line MG63 was transfected and divided into Mock, Control siRNA, si-PAK4, LIMK1, and si-PAK4+LIMK1 groups. Then, the cellular biological features of MG63 cells were detected by CCK-8, wound-healing, Transwell, and flow cytometry methods. The relationship of PAK4 and LIMK1 was performed by co-immunoprecipitation test, and the protein expression of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 was determined by Western blotting. Finally, the effect of PAK4 on the growth of osteosarcoma was verified by subcutaneous transplantation model of osteosarcoma in nude mice.
Results: The expression of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 in both osteosarcoma tissues and cells was up-regulated. Positive PAK4, LIMK1, and Cofilin-1 expressions in osteosarcoma were associated with the clinical stage, distant metastasis, and tumor grade. The MG63 cell viability, migration, and invasion, as well as the expression of PAK4, p-LIMK/LIMK, and p-Cofilin-1/Cofilin-1, were restrained by the knock down of PAK4 while it promoted apoptosis. PAK4 silencing also suppressed the growth of subcutaneous transplanted tumor in nude mice. Co-immunocoprecipitation showed that LIMK and PAK4 protein can form complex in osteosarcoma cells. Besides, LIMK1 overexpression reversed the inhibition effect of PAK4 siRNA on the growth of osteosarcoma cells.
Conclusion: The expression of PAK4/LIMK1/Cofilin-1 pathway in osteosarcoma tissues was up-regulated. Thus, PAK4 inhibition may restrict the osteosarcoma cell proliferation, invasion, and migration but promote its apoptosis via decreasing the activity of LIMK1/Cofilin-1 pathway.
Keywords: Cofilin-1; LIMK1; PAK4; osteosarcoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Wu PK, Chen WM, Lee OK, et al. The prognosis for patients with osteosarcoma who have received prior manipulative therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(11):1580‐1585. - PubMed
-
- Anderson ME. Update on survival in osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am. 2016;47(1):283‐292. - PubMed
-
- Janeway KA, Grier HE. Sequelae of osteosarcoma medical therapy: a review of rare acute toxicities and late effects. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(7):670‐678. - PubMed
-
- Kushlinskii NE, Fridman MV, Braga EA. Molecular mechanisms and microRNAs in osteosarcoma pathogenesis. Biochemistry (Moscow). 2016;81(4):315‐328. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

