Freedom of assembly: metabolic enzymes come together
- PMID: 32463766
- PMCID: PMC7353150
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E18-10-0675
Freedom of assembly: metabolic enzymes come together
Abstract
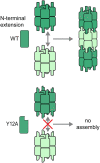
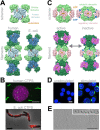
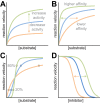
Many different enzymes in intermediate metabolism dynamically assemble filamentous polymers in cells, often in response to changes in physiological conditions. Most of the enzyme filaments known to date have only been observed in cells, but in a handful of cases structural and biochemical studies have revealed the mechanisms and consequences of assembly. In general, enzyme polymerization functions as a mechanism to allosterically tune enzyme kinetics, and it may play a physiological role in integrating metabolic signaling. Here, we highlight some principles of metabolic filaments by focusing on two well-studied examples in nucleotide biosynthesis pathways-inosine-5'-monophosphate (IMP) dehydrogenase and cytosine triphosphate (CTP) synthase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interfilament interaction between IMPDH and CTPS cytoophidia.FEBS J. 2018 Oct;285(20):3753-3768. doi: 10.1111/febs.14624. Epub 2018 Aug 31. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 30085408 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical communication between filament-forming enzymes: Potential Regulatory Roles of Metabolites in Enzyme Co-assemblies with CTP Synthase.Bioessays. 2024 Aug;46(8):e2400063. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400063. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Bioessays. 2024. PMID: 38975656
-
Metabolic regulation via enzyme filamentation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jul-Aug;51(4):282-93. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2016.1172555. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 27098510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly of IMPDH2-based, CTPS-based, and mixed rod/ring structures is dependent on cell type and conditions of induction.J Genet Genomics. 2015 Jun 20;42(6):287-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 18. J Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26165495
-
Molecular cell biology and immunobiology of mammalian rod/ring structures.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014;308:35-74. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800097-7.00002-6. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24411169 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryo-EM structures of CTP synthase filaments reveal mechanism of pH-sensitive assembly during budding yeast starvation.Elife. 2021 Nov 4;10:e73368. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73368. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34734801 Free PMC article.
-
Neurodevelopmental disorder mutations in the purine biosynthetic enzyme IMPDH2 disrupt its allosteric regulation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Aug;299(8):105012. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105012. Epub 2023 Jul 4. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37414152 Free PMC article.
-
Wrangling Shape-Shifting Morpheeins to Tackle Disease and Approach Drug Discovery.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 27;7:582966. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.582966. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33330623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretransition state and apo structures of the filament-forming enzyme SgrAI elucidate mechanisms of activation and substrate specificity.J Biol Chem. 2022 Apr;298(4):101760. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101760. Epub 2022 Feb 21. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35202658 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of L-lactate oxidase by the formation of enzyme assemblies through liquid-liquid phase separation.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 25;13(1):1435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28040-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36697449 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

