Trifluoromethyl Sulfoxides: Reagents for Metal-Free C-H Trifluoromethylthiolation
- PMID: 32463942
- PMCID: PMC7540508
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202005531
Trifluoromethyl Sulfoxides: Reagents for Metal-Free C-H Trifluoromethylthiolation
Abstract
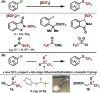
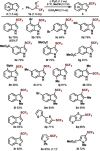
Trifluoromethyl sulfoxides are a new class of trifluoromethylthiolating reagent. The sulfoxides engage in metal-free C-H trifluoromethylthiolation with a range of (hetero)arenes. The method is also applicable to the functionalization of important compound classes, such as ligand derivatives and polyaromatics, and in the late-stage trifluoromethylthiolation of medicines and agrochemicals. The isolation and characterization of a sulfonium salt intermediate supports an interrupted Pummerer reaction mechanism.
Keywords: Pummerer reaction; arenes; reaction mechanisms; sulfoxides; trifluoromethylthiolation.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Purser S., Moore P. R., Swallow S., Gouverneur V., Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 320–330. - PubMed
-
- Preshlock S., Tredwell M., Gouverneur V., Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 719–766. - PubMed
-
- Pertusati F., Serpi M., Pileggi E., Fluorine in Life Sciences: Pharmaceuticals, Medicinal Diagnostics, and Agrochemicals, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019, pp. 141–180.
-
- Sykes J. E., Papich M. G., Canine and Feline Infectious Diseases, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014, pp. 97–104.
-
- Landelle G., Panossian A., Leroux F., Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 941–951. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

