Polymer-Based Bioorthogonal Nanocatalysts for the Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms
- PMID: 32464057
- PMCID: PMC7339739
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.0c01758
Polymer-Based Bioorthogonal Nanocatalysts for the Treatment of Bacterial Biofilms
Abstract
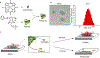
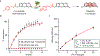
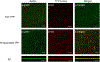
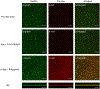
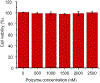
Bioorthogonal catalysis offers a unique strategy to modulate biological processes through the in situ generation of therapeutic agents. However, the direct application of bioorthogonal transition metal catalysts (TMCs) in complex media poses numerous challenges due to issues of limited biocompatibility, poor water solubility, and catalyst deactivation in biological environments. We report here the creation of catalytic "polyzymes", comprised of self-assembled polymer nanoparticles engineered to encapsulate lipophilic TMCs. The incorporation of catalysts into these nanoparticle scaffolds creates water-soluble constructs that provide a protective environment for the catalyst. The potential therapeutic utility of these nanozymes was demonstrated through antimicrobial studies in which a cationic nanozyme was able to penetrate into biofilms and eradicate embedded bacteria through the bioorthogonal activation of a pro-antibiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes
The authors declare no competing final interest.
Figures
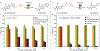
References
-
- Prescher JA; Bertozzi CR Chemistry in Living Systems. Nat. Chem. Biol 2005, 1, 13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

