Mask, a component of the Hippo pathway, is required for Drosophila eye morphogenesis
- PMID: 32464117
- PMCID: PMC7416169
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.05.002
Mask, a component of the Hippo pathway, is required for Drosophila eye morphogenesis
Abstract
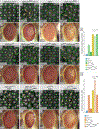
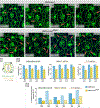
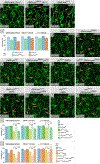
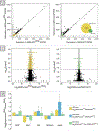
Hippo signaling is an important regulator of tissue size, but it also has a lesser-known role in tissue morphogenesis. Here we use the Drosophila pupal eye to explore the role of the Hippo effector Yki and its cofactor Mask in morphogenesis. We found that Mask is required for the correct distribution and accumulation of adherens junctions and appropriate organization of the cytoskeleton. Accordingly, disrupting mask expression led to severe mis-patterning and similar defects were observed when yki was reduced or in response to ectopic wts. Further, the patterning defects generated by reducing mask expression were modified by Hippo pathway activity. RNA-sequencing revealed a requirement for Mask for appropriate expression of numerous genes during eye morphogenesis. These included genes implicated in cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization, a comprehensive set of genes that promote cell survival, and numerous signal transduction genes. To validate our transcriptome analyses, we then considered two loci that were modified by Mask activity: FER and Vinc, which have established roles in regulating adhesion. Modulating the expression of either locus modified mask mis-patterning and adhesion phenotypes. Further, expression of FER and Vinc was modified by Yki. It is well-established that the Hippo pathway is responsive to changes in cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton, but our data indicate that Hippo signaling also regulates these structures.
Keywords: Drosophila; Eye; Hippo; Mask; Morphogenesis; Yorkie.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Andrews S (2010). FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
-
- Aragona M, Panciera T, Manfrin A, Giulitti S, Michielin F, Elvassore N, Dupont S, and Piccolo S (2013). A mechanical checkpoint controls multicellular growth through YAP/TAZ regulation by actin-processing factors. Cell 154, 1047–1059. - PubMed
-
- Bai H, Zhu Q, Surcel A, Luo T, Ren Y, Guan B, Liu Y, Wu N, Joseph NE, and Wang T-L (2016). Yes-Associated Protein impacts adherens junction assembly through regulating actin cytoskeleton organization. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, ajpgi. 00027.02016. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

