The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity
- PMID: 32466586
- PMCID: PMC7312803
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17113782
The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity
Abstract
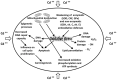
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic non-essential transition metal that poses a health risk for both humans and animals. It is naturally occurring in the environment as a pollutant that is derived from agricultural and industrial sources. Exposure to cadmium primarily occurs through the ingestion of contaminated food and water and, to a significant extent, through inhalation and cigarette smoking. Cadmium accumulates in plants and animals with a long half-life of about 25-30 years. Epidemiological data suggest that occupational and environmental cadmium exposure may be related to various types of cancer, including breast, lung, prostate, nasopharynx, pancreas, and kidney cancers. It has been also demonstrated that environmental cadmium may be a risk factor for osteoporosis. The liver and kidneys are extremely sensitive to cadmium's toxic effects. This may be due to the ability of these tissues to synthesize metallothioneins (MT), which are Cd-inducible proteins that protect the cell by tightly binding the toxic cadmium ions. The oxidative stress induced by this xenobiotic may be one of the mechanisms responsible for several liver and kidney diseases. Mitochondria damage is highly plausible given that these organelles play a crucial role in the formation of ROS (reactive oxygen species) and are known to be among the key intracellular targets for cadmium. When mitochondria become dysfunctional after exposure to Cd, they produce less energy (ATP) and more ROS. Recent studies show that cadmium induces various epigenetic changes in mammalian cells, both in vivo and in vitro, causing pathogenic risks and the development of various types of cancers. The epigenetics present themselves as chemical modifications of DNA and histones that alter the chromatin without changing the sequence of the DNA nucleotide. DNA methyltransferase, histone acetyltransferase, histone deacetylase and histone methyltransferase, and micro RNA are involved in the epigenetic changes. Recently, investigations of the capability of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.), Indian mustard (Brassica juncea), and river red gum (Eucalyptus camaldulensis) to remove cadmium from polluted soil and water have been carried out. Moreover, nanoparticles of TiO2 and Al2O3 have been used to efficiently remove cadmium from wastewater and soil. Finally, microbial fermentation has been studied as a promising method for removing cadmium from food. This review provides an update on the effects of Cd exposure on human health, focusing on the cellular and molecular alterations involved.
Keywords: antioxidant; apoptosis; cadmium; cancer; chelators; damage of mitochondria; metallothioneins; phytoremediation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sinicropi M.S., Caruso A., Capasso A., Palladino C., Panno A., Saturnino C. Heavy metals: Toxicity and carcinogenicity. Pharmacologyonline. 2010;2:329–333.
-
- Carocci A., Rovito N., Sinicropi M.S., Genchi G. Mercury toxicity and neurodegenerative effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014;229:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Carocci A., Catalano A., Lauria G., Sinicropi M.S., Genchi G. Lead Toxicity, antioxidant defense and environment. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016;238:45–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

