The BADC and BCCP subunits of chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase sense the pH changes of the light-dark cycle
- PMID: 32467229
- PMCID: PMC7380191
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012877
The BADC and BCCP subunits of chloroplast acetyl-CoA carboxylase sense the pH changes of the light-dark cycle
Abstract
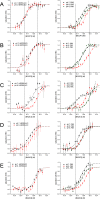
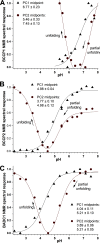
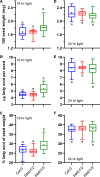
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACCase) catalyzes the first committed step in the de novo synthesis of fatty acids. The multisubunit ACCase in the chloroplast is activated by a shift to pH 8 upon light adaptation and is inhibited by a shift to pH 7 upon dark adaptation. Here, titrations with the purified ACCase biotin attachment domain-containing (BADC) and biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) subunits from Arabidopsis indicated that they can competently and independently bind biotin carboxylase (BC) but differ in responses to pH changes representing those in the plastid stroma during light or dark conditions. At pH 7 in phosphate buffer, BADC1 and BADC2 gain an advantage over BCCP1 and BCCP2 in affinity for BC. At pH 8 in KCl solution, however, BCCP1 and BCCP2 had more than 10-fold higher affinity for BC than did BADC1. The pH-modulated shifts in BC preferences for BCCP and BADC partners suggest they contribute to light-dependent regulation of heteromeric ACCase. Using NMR spectroscopy, we found evidence for increased intrinsic disorder of the BADC and BCCP subunits at pH 7. We propose that this intrinsic disorder potentially promotes fast association with BC through a "fly-casting mechanism." We hypothesize that the pH effects on the BADC and BCCP subunits attenuate ACCase activity by night and enhance it by day. Consistent with this hypothesis, Arabidopsis badc1 badc3 mutant lines grown in a light-dark cycle synthesized more fatty acids in their seeds. In summary, our findings provide evidence that the BADC and BCCP subunits function as pH sensors required for light-dependent switching of heteromeric ACCase activity.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; biophysics; fatty acid biosynthesis; intrinsic disorder; intrinsically disordered protein; lipid synthesis; nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); pH regulation; plant biochemistry; protein–protein interaction; thermodynamics.
© 2020 Ye et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Cahoon E. B., Shockey J. M., Dietrich C. R., Gidda S. K., Mullen R. T., and Dyer J. M. (2007) Engineering oilseeds for sustainable production of industrial and nutritional feedstocks: solving bottlenecks in fatty acid flux. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 10, 236–244 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

