Girdin interaction with vimentin induces EMT and promotes the growth and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32467989
- PMCID: PMC7336503
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2020.7615
Girdin interaction with vimentin induces EMT and promotes the growth and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
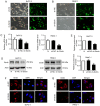
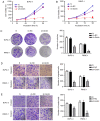
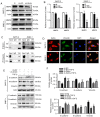
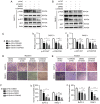
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly malignant cancer of the digestive tract that has a high potential for metastasis and a poor prognosis. Girdin was first reported in 2005 as an actin‑binding protein and was designated as Akt‑phosphorylation enhancer (APE); thus, Girdin has been revealed to have an important role in regulating cancer development. There is additional evidence indicating that Girdin is associated with cell proliferation, migration, invasion and survival in certain cancers. However, the potential mechanisms involving Girdin and mobility in pancreatic cancer have not been elucidated. In the present study, it was revealed that Girdin was highly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissue and was associated with tumor grade. The present study, to the best of our knowledge, is the first aimed at investigating the unknown role of Girdin in PDAC metastasis. A short hairpin RNA for Girdin (sh‑Girdin) was successfully constructed with recombinant adenoviral vectors to suppress the expression of Girdin in pancreatic cancer cell lines (PANC‑1 and BXPC‑3). The silencing efficiency of the Girdin shRNA was determined by RT‑qPCR and western blot analysis, and decreased Girdin expression in the cytoplasm was revealed by immunofluorescence detection. Then, sulforhodamine B (SRB) and colony formation assays were used to confirm that the knockdown of Girdin inhibited proliferation in vitro, and Transwell assays were used to examine the influence of Girdin knockdown on cellular mobility. Animal experiments also confirmed that silencing the expression of Girdin in pancreatic cancer cells inhibited the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer in vivo. Transforming growth factor‑β (TGF‑β) is a common inducer of epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) and can effectively induce EMT in PDAC. Notably, TGF‑β‑treated cells exhibited changes in the classic biological markers of EMT. The expression of E‑cadherin, a marker of the epithelial phenotype, increased, and the expression of N‑cadherin and vimentin, markers of the interstitial phenotype, decreased in response to sh‑Girdin. According to these experiments, Girdin may affect pancreatic cancer progression and development by interacting with vimentin. Therefore, there is evidence indicating that Girdin could be designated as a prognostic biological indicator and a candidate therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Girdin; growth; metastasis; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; EMT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of FOXO3a induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by activation of the β-catenin/TCF4 pathway through SPRY2.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 28;38(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1046-x. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. Retraction in: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 17;41(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02413-2. PMID: 30691517 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Upregulation of integrin β4 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is a novel prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Lab Invest. 2015 Mar;95(3):308-19. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.166. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 25599535
-
Quantitative acetylome and phosphorylome analysis reveals Girdin affects pancreatic cancer progression through regulating Cortactin.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 May 5;12(9):7679-7693. doi: 10.18632/aging.103032. Epub 2020 May 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32369440 Free PMC article.
-
Localisation of PGK1 determines metabolic phenotype to balance metastasis and proliferation in patients with SMAD4-negative pancreatic cancer.Gut. 2020 May;69(5):888-900. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317163. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31611300 Review.
-
The Multifaceted Role of miR-21 in Pancreatic Cancers.Cells. 2024 May 30;13(11):948. doi: 10.3390/cells13110948. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38891080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active legumain promotes invasion and migration of neuroblastoma by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Open Life Sci. 2022 Jun 21;17(1):676-685. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0012. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35800070 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a novel mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA network and identification of potential regulatory axis associated with prognosis in colorectal cancer liver metastases.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jun 3;13(11):14968-14988. doi: 10.18632/aging.203049. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34081622 Free PMC article.
-
FBLN5 is targeted by microRNA‑27a‑3p and suppresses tumorigenesis and progression in high‑grade serous ovarian carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2020 Nov;44(5):2143-2151. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7749. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32901854 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Nature of Nucleobindin-2 in Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 26;22(11):5687. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115687. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLK8 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via the activation of EMT associated with PAR1.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Sep 22;12(10):860. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04149-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34552064 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

