Artificial intelligence radiogenomics for advancing precision and effectiveness in oncologic care (Review)
- PMID: 32467997
- PMCID: PMC7252460
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5063
Artificial intelligence radiogenomics for advancing precision and effectiveness in oncologic care (Review)
Abstract
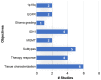
The new era of artificial intelligence (AI) has introduced revolutionary data‑driven analysis paradigms that have led to significant advancements in information processing techniques in the context of clinical decision‑support systems. These advances have created unprecedented momentum in computational medical imaging applications and have given rise to new precision medicine research areas. Radiogenomics is a novel research field focusing on establishing associations between radiological features and genomic or molecular expression in order to shed light on the underlying disease mechanisms and enhance diagnostic procedures towards personalized medicine. The aim of the current review was to elucidate recent advances in radiogenomics research, focusing on deep learning with emphasis on radiology and oncology applications. The main deep learning radiogenomics architectures, together with the clinical questions addressed, and the achieved genetic or molecular correlations are presented, while a performance comparison of the proposed methodologies is conducted. Finally, current limitations, potentially understudied topics and future research directions are discussed.
Keywords: medical imaging/radiogenomics; artificial intelligence; deep learning; machine learning; precision medicine; oncology.
Figures



References
-
- Zhou M, Leung A, Echegaray S, Gentles A, Shrager JB, Jensen KC, Berry GJ, Plevritis SK, Rubin DL, Napel S, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer radiogenomics map identifies relationships between molecular and imaging phenotypes with prognostic implications. Radiology. 2018;286:307–315. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2017161845. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
