Admission chest CT score predicts 5-day outcome in patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 32468085
- PMCID: PMC8824444
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-020-06118-y
Admission chest CT score predicts 5-day outcome in patients with COVID-19
Conflict of interest statement
None.
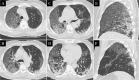
Figures
Comment in
-
Pulmonary embolism detected by CT pulmonary angiography in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.Pulmonology. 2021 Jul-Aug;27(4):348-351. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2021.03.007. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Pulmonology. 2021. PMID: 33910773 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed on 27 April 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

