Older adults with sarcopenia have distinct skeletal muscle phosphodiester, phosphocreatine, and phospholipid profiles
- PMID: 32468656
- PMCID: PMC7294783
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13135
Older adults with sarcopenia have distinct skeletal muscle phosphodiester, phosphocreatine, and phospholipid profiles
Abstract
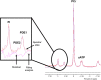
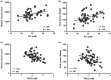
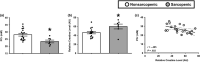
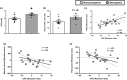
The loss of skeletal muscle mass and function with age (sarcopenia) is a critical healthcare challenge for older adults. 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31 P-MRS) is a powerful tool used to evaluate phosphorus metabolite levels in muscle. Here, we sought to determine which phosphorus metabolites were linked with reduced muscle mass and function in older adults. This investigation was conducted across two separate studies. Resting phosphorus metabolites in skeletal muscle were examined by 31 P-MRS. In the first study, fifty-five older adults with obesity were enrolled and we found that resting phosphocreatine (PCr) was positively associated with muscle volume and knee extensor peak power, while a phosphodiester peak (PDE2) was negatively related to these variables. In the second study, we examined well-phenotyped older adults that were classified as nonsarcopenic or sarcopenic based on sex-specific criteria described by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. PCr content was lower in muscle from older adults with sarcopenia compared to controls, while PDE2 was elevated. Percutaneous biopsy specimens of the vastus lateralis were obtained for metabolomic and lipidomic analyses. Lower PCr was related to higher muscle creatine. PDE2 was associated with glycerol-phosphoethanolamine levels, a putative marker of phospholipid membrane damage. Lipidomic analyses revealed that the major phospholipids, (phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylglycerol) were elevated in sarcopenic muscle and were inversely related to muscle volume and peak power. These data suggest phosphorus metabolites and phospholipids are associated with the loss of skeletal muscle mass and function in older adults.
Keywords: aging; muscle volume; peak power; phosphatidylcholine; phosphatidylethanolamine; phosphodiester.
© 2020 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
P.M. Coen is a consultant for Astellas/Mitobridge, Incorporated.
Figures
Comment in
-
Muscle phosphorus metabolites in sarcopenia.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Aug 28;12(16):15880-15881. doi: 10.18632/aging.104032. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32860671 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aliev, M. , Guzun, R. , Karu‐Varikmaa, M. , Kaambre, T. , Wallimann, T. , & Saks, V. (2011). Molecular system bioenergics of the heart: Experimental studies of metabolic compartmentation and energy fluxes versus computer modeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12, 9296–9331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baburina, I. , & Jackowski, S. (1999). Cellular responses to excess phospholipid. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 9400–9408. - PubMed
-
- Burt, C. T. (1985). Phosphodiesters and NMR: A tale of rabbits and chickens. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 10, 404–406.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

