Survival Outcomes Associated With 3 Years vs 1 Year of Adjuvant Imatinib for Patients With High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: An Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial After 10-Year Follow-up
- PMID: 32469385
- PMCID: PMC7260691
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2091
Survival Outcomes Associated With 3 Years vs 1 Year of Adjuvant Imatinib for Patients With High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: An Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial After 10-Year Follow-up
Abstract
Importance: Adjuvant imatinib is associated with improved recurrence-free survival (RFS) when administered after surgery to patients with operable gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), but its influence on overall survival (OS) has remained uncertain.
Objective: To evaluate the effect of adjuvant imatinib on OS of patients who have a high estimated risk for GIST recurrence after macroscopically complete surgery.
Design, setting, and participants: In this open-label, randomized (1:1), multicenter phase 3 clinical trial conducted in Finland, Germany, Norway, and Sweden, 400 patients who had undergone macroscopically complete surgery for GIST with a high estimated risk for recurrence according to the modified National Institutes of Health Consensus Criteria were enrolled between February 2004 and September 2008. Data for this follow-up analysis were analyzed from September to November, 2019.
Interventions: Imatinib 400 mg/d administered orally for either 12 months or 36 months after surgery.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was RFS; the secondary objectives included OS and treatment safety.
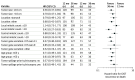
Results: The intention-to-treat cohort consisted of 397 patients (12-month group, 199; 36-month group, 198; 201 men and 196 women; median [IQR] age, 62 (51-69) years and 60 (51-67) years, during a median follow-up time of 119 months after the date of randomization, 194 RFS events and 96 OS events were recorded in the intention-to-treat population. Five-year and 10-year RFS was 71.4% and 52.5%, respectively, in the 36-month group and 53.0% and 41.8% in the 12-month group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.66; 95% CI, 0.49-0.87; P = .003). In the 36-month group, 5-year OS and 10-year OS rates were 92.0% and 79.0%, respectively, and in the 12-month group 85.5% and 65.3% (HR, 0.55; 95% CI, 0.37-0.83; P = .004). The results were similar in the efficacy population, from which 15 patients who did not have GIST in central pathology review and 24 patients who had intra-abdominal metastases removed at surgery were excluded (36-month group, 10-year OS 81.6%; 12-month group, 66.8%; HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.32-0.80; P = .003). No new safety signals were detected.
Conclusions and relevance: Three years of adjuvant imatinib is superior in efficacy compared with 1 year of imatinib. Approximately 50% of deaths may be avoided during the first 10 years of follow-up after surgery with longer adjuvant imatinib treatment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00116935.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Dematteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, et al. ; American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG) Intergroup Adjuvant GIST Study Team . Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of localised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;373(9669):1097-1104. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60500-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casali PG, Le Cesne A, Poveda Velasco A, et al. Time to definitive failure to the first tyrosine kinase inhibitor in localized GI stromal tumors treated with imatinib as an adjuvant: a European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group Intergroup randomized trial in collaboration with the Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials Group, UNICANCER, French Sarcoma Group, Italian Sarcoma Group, and Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(36):4276-4283. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.4304 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

