Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Immunotherapy Rechallenge in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 32469396
- PMCID: PMC7260689
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.2169
Evaluation of the Safety and Efficacy of Immunotherapy Rechallenge in Patients With Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Importance: Several immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are approved for use in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC), but the efficacy and safety of ICI rechallenge in mRCC is unknown.
Objective: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of ICI rechallenge in patients with mRCC.
Design, setting, and participants: This multicenter, retrospective cohort study included consecutive patients with mRCC from 9 institutions in the US who received at least 2 separate lines of ICI (ICI-1, ICI-2) between January 2012 and December 2019.
Exposure: Receipt of an ICI (anticytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4, anti-programmed cell death protein 1, or anti-programmed cell death ligand 1), alone or in combination with other therapies, in at least 2 separate lines of therapy for mRCC.
Main outcomes and measures: Investigator-assessed best overall response and immune-related adverse events.
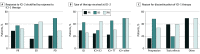
Results: A total of 69 patients were included. Median (range) age at diagnosis of mRCC was 61 (36-86) years. Of these, 50 were men and 19 were women. The most common therapies received at ICI-1 were single-agent ICI (n = 27 [39%]) or ICI in combination with targeted therapy (n = 29 [42%]), while at ICI-2, the most common therapies were single-agent ICI (n = 26 [38%]) or dual ICI (n = 22 [32%]). Most patients discontinued ICI-1 owing to disease progression (n = 50 [72%]) or toxic effects (n = 16 [23%]). The overall response rates at ICI-1 and ICI-2 were 37% and 23%, respectively. The likelihood of a response at ICI-2 was greatest among patients who had previously responded to ICI-1 (7 of 24 [29%]), although responses at ICI-2 were seen in those who had progressive disease as their best response following ICI-1 (3 of 14 [21%]) as well as in those who received single-agent ICI at ICI-2 (7 of 23 [30%]). Grade 3 or higher immune-related adverse events were seen in 18 patients (26%) and 11 patients (16%) at ICI-1 and ICI-2, respectively. There were no treatment-related deaths.
Conclusions and relevance: The findings of this multicenter cohort study suggest that ICI rechallenge in patients with mRCC may be safe and reasonably efficacious, with an overall response rate of 23%. Data from prospective studies are needed to validate these findings and determine the role of sequential ICI regimens in treatment of mRCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
ICI rechallenge in mRCC.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep;17(9):520. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0407-x. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32561866 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tannir NM, Frontera OA, Hammers HJ, et al. Thirty-month follow-up of the phase III CheckMate 214 trial of first-line nivolumab + ipilimumab (N+I) or sunitinib (S) in patients (pts) with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). J Clin Oncol. 2020;37(7):2547.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

