Hypoxia-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer
- PMID: 32470488
- PMCID: PMC7336507
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.05.012
Hypoxia-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in cancer
Abstract
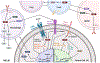
A common feature of many solid tumors is low oxygen conditions due to inadequate blood supply. Hypoxia induces hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) stabilization and downstream signaling. This signaling has pleiotropic roles in cancers, including the promotion of cellular proliferation, changes in metabolism, and induction of angiogenesis. In addition, hypoxia is becoming recognized as an important driver of epithelial-to-mesenchymal (EMT) in cancer. During EMT, epithelial cells lose their typical polarized states and transition to a more mobile mesenchymal phenotype. Hypoxia induces this transition by modulating EMT signaling pathways, inducing EMT transcription factor activity, and regulating miRNA networks. As both hypoxia and EMT modulate the tumor microenvironment (TME) and are associated with immunosuppression, we also explore how these pathways may impact response to immuno-oncology therapeutics.
Keywords: Cancer; EMT; HIF; Hypoxia; Immunosuppression; Metastasis.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest We have no significant conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

