CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Correction to Understand ALS
- PMID: 32471232
- PMCID: PMC7312396
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113801
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Correction to Understand ALS
Abstract
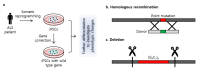
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the death of motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem. ALS has a diverse genetic origin; at least 20 genes have been shown to be related to ALS. Most familial and sporadic cases of ALS are caused by variants of the SOD1, C9orf72, FUS, and TARDBP genes. Genome editing using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated system 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) can provide insights into the underlying genetics and pathophysiology of ALS. By correcting common mutations associated with ALS in animal models and patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), CRISPR/Cas9 has been used to verify the effects of ALS-associated mutations and observe phenotype differences between patient-derived and gene-corrected iPSCs. This technology has also been used to create mutations to investigate the pathophysiology of ALS. Here, we review recent studies that have used CRISPR/Cas9 to understand the genetic underpinnings of ALS.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); gene correction; induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted gene correction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patient iPSCs.Protein Cell. 2017 May;8(5):365-378. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0397-3. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Protein Cell. 2017. PMID: 28401346 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Therapy in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cells. 2022 Jun 29;11(13):2066. doi: 10.3390/cells11132066. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correction of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis related phenotypes in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived motor neurons carrying a hexanucleotide expansion mutation in C9orf72 by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing using homology-directed repair.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Aug 3;29(13):2200-2217. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa106. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32504093 Free PMC article.
-
Targets and Gene Therapy of ALS (Part 1).Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 25;26(9):4063. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094063. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo genome editing improves motor function and extends survival in a mouse model of ALS.Sci Adv. 2017 Dec 20;3(12):eaar3952. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar3952. eCollection 2017 Dec. Sci Adv. 2017. PMID: 29279867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 technology: applications in oocytes and early embryos.J Transl Med. 2023 Oct 24;21(1):746. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04610-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37875936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Strategies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 24;10(7):1012. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071012. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34202494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 system and its applications in nervous system diseases.Genes Dis. 2023 Apr 13;11(2):675-686. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.017. eCollection 2024 Mar. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37692518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketogenic diet for human diseases: the underlying mechanisms and potential for clinical implementations.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jan 17;7(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00831-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35034957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dead Cas(t) light on new life: CRISPRa-mediated reprogramming of somatic cells into neurons.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 May 24;79(6):315. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04324-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35610381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hulisz D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Disease state overview. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2018;24:S320–S326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

