Impact of a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Trichostatin A on Neurogenesis after Hypoxia-Ischemia in Immature Rats
- PMID: 32471267
- PMCID: PMC7312253
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113808
Impact of a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor-Trichostatin A on Neurogenesis after Hypoxia-Ischemia in Immature Rats
Abstract
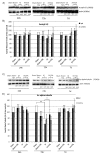
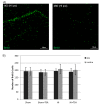
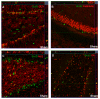
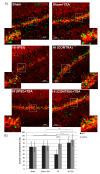
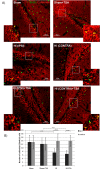
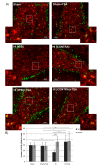
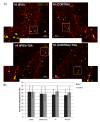
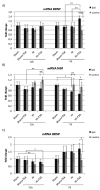
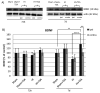
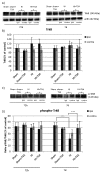
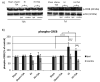
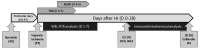
Hypoxia-ischemia (HI) in the neonatal brain frequently results in neurologic impairments, including cognitive disability. Unfortunately, there are currently no known treatment options to minimize ischemia-induced neural damage. We previously showed the neuroprotective/neurogenic potential of a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi), sodium butyrate (SB), in a neonatal HI rat pup model. The aim of the present study was to examine the capacity of another HDACi-Trichostatin A (TSA)-to stimulate neurogenesis in the subgranular zone of the hippocampus. We also assessed some of the cellular/molecular processes that could be involved in the action of TSA, including the expression of neurotrophic factors (glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)) as well as the TrkB receptor and its downstream signalling substrate- cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). Seven-day-old rat pups were subjected to unilateral carotid artery ligation followed by hypoxia for 1 h. TSA was administered directly after the insult (0.2 mg/kg body weight). The study demonstrated that treatment with TSA restored the reduced by hypoxia-ischemia number of immature neurons (neuroblasts, BrdU/DCX-positive) as well as the number of oligodendrocyte progenitors (BrdU/NG2+) in the dentate gyrus of the ipsilateral damaged hemisphere. However, new generated cells did not develop the more mature phenotypes. Moreover, the administration of TSA stimulated the expression of BDNF and increased the activation of the TrkB receptor. These results suggest that BDNF-TrkB signalling pathways may contribute to the effects of TSA after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury.
Keywords: BDNF-TrkB pathway; CREB; neonatal hypoxia-ischemia; neurogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of the HDAC Inhibitor, Sodium Butyrate, on Neurogenesis in a Rat Model of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia: Potential Mechanism of Action.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Sep;56(9):6341-6370. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1518-1. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30767185 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Butyrate, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Exhibits Neuroprotective/Neurogenic Effects in a Rat Model of Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):5300-5318. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0049-2. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27578020 Free PMC article.
-
The HDAC inhibitor, sodium butyrate, stimulates neurogenesis in the ischemic brain.J Neurochem. 2009 Aug;110(4):1226-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06212.x. Epub 2009 Jun 15. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19549282 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection Against Hypoxic/Ischemic Injury: δ-Opioid Receptors and BDNF-TrkB Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(1):302-315. doi: 10.1159/000489808. Epub 2018 May 11. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29768254 Review.
-
Growth Factors in the Carotid Body-An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 1;21(19):7267. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197267. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33019660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergic Neuroprotection Between Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort and Borneol Against Ischemic Stroke by Neurogenesis via Modulating Reactive Astrogliosis and Maintaining the Blood-Brain Barrier.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 16;12:666790. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.666790. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34220506 Free PMC article.
-
Teratoma Growth Retardation by HDACi Treatment of the Tumor Embryonal Source.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 18;12(11):3416. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113416. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33217978 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets in stroke.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022 Nov;42(11):2000-2016. doi: 10.1177/0271678X221116192. Epub 2022 Jul 19. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2022. PMID: 35854641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lactate metabolism and protein lactylation in epilepsy.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Jan 14;18:1464169. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1464169. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39876842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates cognitive impairment by promoting hippocampal neurogenesis via BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling pathway in hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jan;30(1):e14486. doi: 10.1111/cns.14486. Epub 2023 Oct 13. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37830170 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

