Urinary MicroRNAs as Potential Markers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 32471285
- PMCID: PMC7312501
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113814
Urinary MicroRNAs as Potential Markers for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
Abstract
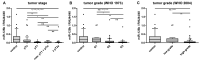
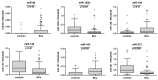
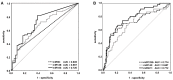
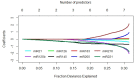
Currently, voided urine cytology (VUC) serves as the gold standard for the detection of bladder cancer (BCa) in urine. Despite its high specificity, VUC has shortcomings in terms of sensitivity. Therefore, alternative biomarkers are being searched, which might overcome these disadvantages as a useful adjunct to VUC. The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic potential of the urinary levels of selected microRNAs (miRs), which might represent such alternative biomarkers due to their BCa-specific expression. Expression levels of nine BCa-associated microRNAs (miR-21, -96, -125b, -126, -145, -183, -205, -210, -221) were assessed by quantitative PCR in urine sediments from 104 patients with primary BCa and 46 control subjects. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses revealed a diagnostic potential for miR-96, -125b, -126, -145, -183, and -221 with area under the curve (AUC) values between 0.605 and 0.772. The combination of the four best candidates resulted in sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values (NPV), and accuracy of 73.1%, 95.7%, 97.4%, 61.1%, and 80.0%, respectively. Combined with VUC, sensitivity and NPV could be increased by nearly 8%, each surpassing the performance of VUC alone. The present findings suggested a diagnostic potential of miR-125b, -145, -183, and -221 in combination with VUC for non-invasive detection of BCa in urine.
Keywords: miRNA; quantitative PCR; tumor marker; urothelial carcinoma; voided urine cytology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The performance of the Xpert Bladder Cancer Monitor Test and voided urinary cytology in the follow-up of urinary bladder tumors.Radiol Oncol. 2020 Dec 29;55(2):196-202. doi: 10.2478/raon-2020-0072. Radiol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33764701 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary mRNA biomarker panel for the detection of urothelial carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 21;7(25):38731-38740. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9587. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27231851 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of urinary nuclear matrix protein-22 and bladder tumour antigen tests with voided urinary cytology in detecting and following bladder cancer: the prognostic value of false-positive results.BJU Int. 2001 Nov;88(7):692-701. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02355.x. BJU Int. 2001. PMID: 11890239
-
Urinary extracellular vesicles-encapsulated miRNA signatures: A new paradigm for urinary bladder cancer diagnosis and classification.Urol Oncol. 2024 Jul;42(7):179-190. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2024.03.006. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Urol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38594151 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for the Diagnostics of Bladder Cancer: a Meta-Analysis.Clin Lab. 2015;61(8):1101-8. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2015.150204. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 26427157 Review.
Cited by
-
Validation of a microRNA profile in urine liquid biopsy with diagnostic and stratification value for bladder cancer classification, available through the open app BladdermiRaCan.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Apr 11;14(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00649-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40217499 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Stratification of Bladder Cancer Patients with a MicroRNA-based Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 26;12(11):3133. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113133. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33114775 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in non-invasive diagnosis of bladder cancer: a systematic review.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024 Nov 29;22:eRW0611. doi: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2024RW0611. eCollection 2024. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2024. PMID: 39630752 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles: New Endogenous Shuttles for miRNAs in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6486. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186486. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular profiles and urinary biomarkers of upper tract urothelial carcinomas associated with aristolochic acid exposure.Int J Cancer. 2022 Jan 15;150(2):374-386. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33827. Epub 2021 Oct 15. Int J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34569060 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

