Resolving DNA Damage: Epigenetic Regulation of DNA Repair
- PMID: 32471288
- PMCID: PMC7321228
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25112496
Resolving DNA Damage: Epigenetic Regulation of DNA Repair
Abstract
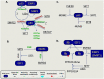
Epigenetic research has rapidly evolved into a dynamic field of genome biology. Chromatin regulation has been proved to be an essential aspect for all genomic processes, including DNA repair. Chromatin structure is modified by enzymes and factors that deposit, erase, and interact with epigenetic marks such as DNA and histone modifications, as well as by complexes that remodel nucleosomes. In this review we discuss recent advances on how the chromatin state is modulated during this multi-step process of damage recognition, signaling, and repair. Moreover, we examine how chromatin is regulated when different pathways of DNA repair are utilized. Furthermore, we review additional modes of regulation of DNA repair, such as through the role of global and localized chromatin states in maintaining expression of DNA repair genes, as well as through the activity of epigenetic enzymes on non-nucleosome substrates. Finally, we discuss current and future applications of the mechanistic interplays between chromatin regulation and DNA repair in the context cancer treatment.
Keywords: DNA damage; DNA repair; chromatin remodeling; epigenomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

