Microstructural changes in the trigeminal nerve of patients with episodic migraine assessed using magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 32471359
- PMCID: PMC7260805
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-020-01126-1
Microstructural changes in the trigeminal nerve of patients with episodic migraine assessed using magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background: There is histological evidence of microstructural changes in the zygomaticotemporal branch of the trigeminal nerve in migraineurs. This raises the possibility that altered trigeminal nerve properties contribute to migraine pathophysiology. Whilst it is not possible to explore the anatomy of small trigeminal nerve branches it is possible to explore the anatomy of the trigeminal root entry zone using magnetic resonance imaging in humans. The aim of this investigation is to assess the microstructure of the trigeminal nerve in vivo to determine if nerve alterations occur in individuals with episodic migraine.
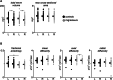
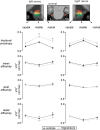
Methods: In 39 migraineurs and 39 matched controls, T1-weighted anatomical images were used to calculate the volume (mm3) and maximal cross-sectional area of the trigeminal nerve root entry zone; diffusion tensor images were used to calculate fractional anisotropy, mean diffusion, axial diffusion and radial diffusion.
Results: There were significant differences between the left and right nerve of controls and migraineurs with respect to volume and not cross-sectional area. Migraineurs displayed reduced axial diffusion in the right nerve compared to the left nerve, and reduced fractional anisotropy in the left nerve compared to left controls. Furthermore, although there were no differences in mean diffusion or radial diffusion, regional analysis of the nerve revealed significantly greater radial diffusion in the middle and rostral portion of the left trigeminal nerve in migraineurs compared with controls.
Conclusions: Migraine pathophysiology is associated with microstructural abnormalities within the trigeminal nerve that are consistent with histological evidence of altered myelin and/or organization. These peripheral nerve changes may provide further insight into migraine pathophysiology and enable a greater understanding for targeted treatments of pain alleviation.
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; Fractional anisotropy; Mean diffusivity; Nerve volume; Trigeminal root entry zone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Erbay SH, Bhadelia RA, O’Callaghan M, Gupta P, Riesenburger R, Krackov W, et al. Nerve atrophy in severe trigeminal neuralgia: noninvasive confirmation at MR imaging--initial experience. Radiology. 2006;238(2):689–692. - PubMed
-
- Leal PR, Roch JA, Hermier M, Souza MA, Cristino-Filho G, Sindou M. Structural abnormalities of the trigeminal root revealed by diffusion tensor imaging in patients with trigeminal neuralgia caused by neurovascular compression: a prospective, double-blind, controlled study. Pain. 2011;152(10):2357–2364. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Li D, Bao F, Guo C, Ma S, Zhang M. Microstructural abnormalities of the trigeminal nerve correlate with pain severity and concomitant emotional dysfunctions in idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: a randomized, prospective, double-blind study. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;34(5):609–616. - PubMed
-
- Wilcox SL, Gustin SM, Eykman EN, Fowler G, Peck CC, Murray GM, et al. Trigeminal nerve anatomy in neuropathic and non-neuropathic orofacial pain patients. J Pain. 2013;14(8):865–872. - PubMed

