Neutrophil FcγRIIA availability is associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 32471491
- PMCID: PMC7257165
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02221-z
Neutrophil FcγRIIA availability is associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Immune complexes (ICs) are detectable in a variety of inflammatory diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), reflecting autoantibody binding to antigens. Though ICs are the main contributors to disease pathogenesis through FcγR-mediated inflammation and organ damage, IC levels are not part of the clinical assessment of SLE. The aim of this study was to explore the clinical utility of analyzing levels of ICs in SLE patients using a novel technology, IC-FLOW.
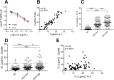
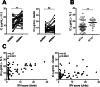
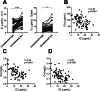
Methods: Paired serum samples, at the time point of high and low disease activity (n = 92), were analyzed using two assays: an IC ELISA from a commercial company and a novel in-house flow cytometry-based method, IC-FLOW. IC-FLOW measures FcγRIIA availability on the neutrophil cell surface by flow cytometry, whereas the commercial ELISA measures IC binding to C1q.
Results: Using IC-FLOW, 90% of SLE patients with active disease had elevated levels of circulating ICs (p < 0.0001). Using the commercial assay, only 17% of SLE patients had elevated levels of circulating ICs. For both assays, levels of ICs reflected active disease as determined by SLEDAI (r = 0.45, p < 0.0001) and were associated with type I IFN activity (r = 0.37, p = 0.001), and complement consumption (p = 0.0002). Levels of ICs measured with IC-FLOW, but not with the commercial ELISA, were associated with active lupus nephritis (p = 0.004).
Conclusions: This novel FcγRIIA-IC assay can detect levels of circulating ICs in patients with SLE. Analyzing IC levels may facilitate monitoring of disease activity, as well as identify patients at risk of lupus nephritis, allowing for early preventive interventions.
Keywords: Biomarker; Immune complex; Interferon; Nephritis; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
CL holds a patent pending for the IC-FLOW technology. The other authors (AAB, HT) declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immune complexes-mediated activation of neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus is dependent on RNA recognition by toll-like receptor 8.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1515469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1515469. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39776899 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus-Associated Immune Complexes Activate Human Neutrophils in an FcγRIIA-Dependent but TLR-Independent Response.J Immunol. 2019 Feb 1;202(3):675-683. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800300. Epub 2019 Jan 4. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30610165 Free PMC article.
-
IgG glycan hydrolysis by endoglycosidase S diminishes the proinflammatory properties of immune complexes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a possible new treatment?Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Aug;64(8):2698-706. doi: 10.1002/art.34454. Arthritis Rheum. 2012. PMID: 22392566
-
Circulating microparticles in systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Dan Med J. 2012 Nov;59(11):B4548. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 23171755 Review.
-
Association of FcγRIIA-R/H131 polymorphism and systemic lupus erythematosus lupus nephritis risk: A meta-analysis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2020 Jul;23(7):853-867. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13815. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Int J Rheum Dis. 2020. PMID: 32189478 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune complexes-mediated activation of neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus is dependent on RNA recognition by toll-like receptor 8.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 24;15:1515469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1515469. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39776899 Free PMC article.
-
AL008 Enhances Myeloid Antitumor Function by Inhibiting SIRPα Signaling and Activating Fc Receptors.J Immunol. 2023 Jan 15;210(2):204-215. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200157. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36480261 Free PMC article.
-
Immune complex-mediated neutrophil activation in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023 Aug 1;62(8):2880-2886. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac722. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 36562570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lovgren T, Eloranta ML, Bave U, Alm GV, Ronnblom L. Induction of interferon-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by immune complexes containing nucleic acid released by necrotic or late apoptotic cells and lupus IgG. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(6):1861–1872. - PubMed
-
- Lood C, Gullstrand B, Truedsson L, Olin AI, Alm GV, Ronnblom L, et al. C1q inhibits immune complex-induced interferon-alpha production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells: a novel link between C1q deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(10):3081–3090. - PubMed
-
- Lock RJ, Unsworth DJ. Measurement of immune complexes is not useful in routine clinical practice. Ann Clin Biochem. 2000;37(Pt 3):253–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

