Detection of air and surface contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in hospital rooms of infected patients
- PMID: 32472043
- PMCID: PMC7260225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16670-2
Detection of air and surface contamination by SARS-CoV-2 in hospital rooms of infected patients
Abstract
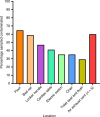
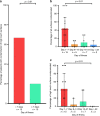
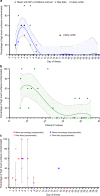
Understanding the particle size distribution in the air and patterns of environmental contamination of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection prevention policies. Here we screen surface and air samples from hospital rooms of COVID-19 patients for SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Environmental sampling is conducted in three airborne infection isolation rooms (AIIRs) in the ICU and 27 AIIRs in the general ward. 245 surface samples are collected. 56.7% of rooms have at least one environmental surface contaminated. High touch surface contamination is shown in ten (66.7%) out of 15 patients in the first week of illness, and three (20%) beyond the first week of illness (p = 0.01, χ2 test). Air sampling is performed in three of the 27 AIIRs in the general ward, and detects SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive particles of sizes >4 µm and 1-4 µm in two rooms, despite these rooms having 12 air changes per hour. This warrants further study of the airborne transmission potential of SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests as defined by Nature Research, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper. The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures
Comment in
-
Recognizing and controlling airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in indoor environments.Indoor Air. 2020 Jul;30(4):557-558. doi: 10.1111/ina.12697. Indoor Air. 2020. PMID: 32557915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ong Sean Wei Xiang, Tan Yian Kim, Chia Po Ying, Lee Tau Hong, Ng Oon Tek, Wong Michelle Su Yen, Marimuthu Kalisvar. Air, Surface Environmental, and Personal Protective Equipment Contamination by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) From a Symptomatic Patient. JAMA. 2020;323(16):1610. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3227. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Young Barnaby Edward, Ong Sean Wei Xiang, Kalimuddin Shirin, Low Jenny G., Tan Seow Yen, Loh Jiashen, Ng Oon-Tek, Marimuthu Kalisvar, Ang Li Wei, Mak Tze Minn, Lau Sok Kiang, Anderson Danielle E., Chan Kian Sing, Tan Thean Yen, Ng Tong Yong, Cui Lin, Said Zubaidah, Kurupatham Lalitha, Chen Mark I-Cheng, Chan Monica, Vasoo Shawn, Wang Lin-Fa, Tan Boon Huan, Lin Raymond Tzer Pin, Lee Vernon Jian Ming, Leo Yee-Sin, Lye David Chien. Epidemiologic Features and Clinical Course of Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore. JAMA. 2020;323(15):1488. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.3204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan Jasper Fuk-Woo, Yuan Shuofeng, Kok Kin-Hang, To Kelvin Kai-Wang, Chu Hin, Yang Jin, Xing Fanfan, Liu Jieling, Yip Cyril Chik-Yan, Poon Rosana Wing-Shan, Tsoi Hoi-Wah, Lo Simon Kam-Fai, Chan Kwok-Hung, Poon Vincent Kwok-Man, Chan Wan-Mui, Ip Jonathan Daniel, Cai Jian-Piao, Cheng Vincent Chi-Chung, Chen Honglin, Hui Christopher Kim-Ming, Yuen Kwok-Yung. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. The Lancet. 2020;395(10223):514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NMRC Research Training Fellowship (NMRC/Fellowship/0056/2018)/MOH | National Medical Research Council (NMRC)/International
- NMRC Clinician Scientist Award (MOH-000276)/MOH | National Medical Research Council (NMRC)/International
- NMRC CS-IRG (CIRG18Nov-0034)/MOH | National Medical Research Council (NMRC)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

