Neoplastic fibrocytes play an essential role in bone marrow fibrosis in Jak2V617F-induced primary myelofibrosis mice
- PMID: 32472085
- PMCID: PMC7862060
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-020-0880-3
Neoplastic fibrocytes play an essential role in bone marrow fibrosis in Jak2V617F-induced primary myelofibrosis mice
Abstract
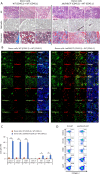
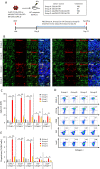
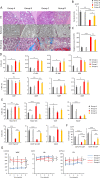
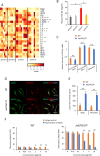
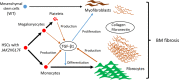
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) characterized by clonal myeloproliferation, progressive bone marrow (BM) fibrosis, splenomegaly, and anemia. BM fibrosis was previously thought to be a reactive phenomenon induced by mesenchymal stromal cells that are stimulated by the overproduction of cytokines such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. However, the involvement of neoplastic fibrocytes in BM fibrosis was recently reported. In this study, we showed that the vast majority of collagen- and fibronectin-producing cells in the BM and spleens of Jak2V617F-induced myelofibrosis (MF) mice were fibrocytes derived from neoplastic hematopoietic cells. Neoplastic monocyte depletion eliminated collagen- and fibronectin-producing fibrocytes in BM and spleen, and ameliorated most characteristic MF features in Jak2V617F transgenic mice, including BM fibrosis, anemia, and splenomegaly, while had little effect on the elevated numbers of megakaryocytes and stem cells in BM, and leukothrombocytosis in peripheral blood. TGF-β1, which was produced by hematopoietic cells including fibrocytes, promoted the differentiation of neoplastic monocytes to fibrocytes, and elevated plasma TGF-β1 levels were normalized by monocyte depletion. Collectively, our data suggest that neoplastic fibrocytes are the major contributor to BM fibrosis in PMF, and TGF-β1 is required for their differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017. pp. 39–53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

