Functional outcome after corrective osteotomy for malunion of the distal radius: a randomised, controlled, double-blind trial
- PMID: 32472263
- PMCID: PMC7306028
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-020-04605-x
Functional outcome after corrective osteotomy for malunion of the distal radius: a randomised, controlled, double-blind trial
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this randomised, controlled, double-blind trial was to evaluate functional outcome during the first year after corrective osteotomy for malunited distal radius fractures, with or without filling the osteotomy void.
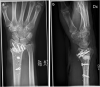
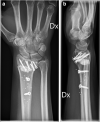
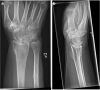
Method: Patients were randomised to receive a HydroSet bone substitute or no graft. Cortical contact was maintained and stabilisation of the osteotomy was carried out with a DiPhos R- or RM Plate. To evaluate subjective functional outcome, the Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation (PRWE), the Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (Q-DASH), the Canadian Occupational Performance Measure (COPM) and the RAND-36 were used. Moreover, range of motion and grip strength were measured by blinded evaluators. Evaluations were made pre-operatively and three, six and 12 months post-operatively.
Results: There were no significant differences between the groups at any time point post-operatively with respect to any of the PROMs that were used or range of motion or grip strength (p > 0.05). In both groups, there was a significant improvement at the 12-month follow-up compared with pre-operatively for the PRWE, the Q-DASH and the COPM satisfaction scores. The RAND-36 revealed no significant differences except for two domains, in which there was an improvement in the treatment group (p < 0.05). For grip strength and for range of motion in all movement directions, except dorsal extension, there was a significant improvement in both groups (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: There is no significant difference in functional outcome during the first year after corrective open-wedge distal radius osteotomy, where cortical contact is maintained, regardless of whether or not bone substitute to fill the void is used.
Keywords: Corrective osteotomy; Distal radius; Grip strength; Malunion; Range of motion; Subjective outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Taras JS, Ladd AL, Kalainov DM, Ruch DS, Ring DC. New concepts in the treatment of distal radius fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2010;59:313–332. - PubMed
-
- Brogren E, Hofer M, Petranek M, Wagner P, Dahlin LB, Atroshi I. Relationship between distal radius fracture malunion and arm-related disability: a prospective population-based cohort study with 1-year follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:1–9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

