Neuropilin1 silencing impairs the proliferation and migration of cells in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 32472711
- PMCID: PMC7521280
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23394
Neuropilin1 silencing impairs the proliferation and migration of cells in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Neuropilin1 (NRP1) participates in cancer cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis as a multifunctional co-receptor by interacting with multiple signal pathways, but few studies have addressed the precise function of NRP1 in pancreatic cancer (PACA) cells. We aimed to study whether NRP1 gene silencing involved in the proliferation and migration of PACA cells in vitro.
Methods: A lentiviral vector expressing NRP1 shRNA was constructed and transfected into human PACA cells (CFPAC-1 and PANC-1). The expression of NRP1 protein and mRNA was detected by Western blot and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) assay, respectively. CCK-8 assay, wound healing assay, and transwell assay were conducted to examine the effect of NRP1 silencing on cells proliferation and migration capability.
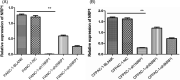
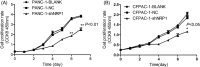
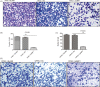
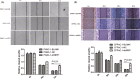
Results: Results of qRT-PCR and Western blot showed successfully established, stably transfected shRNA-NRP1 cells in PACA cells. The proliferation capacity of PACA cells in NRP1 shRNA group was lower significantly than that in the negative control (NC) group (P < .05). The invasion and migration capability of PACA cells in NRP1 shRNA group was lower significantly than that in the NC group (P < .01).
Conclusions: NRP1-shRNA lentiviral interference vectors can effectively decrease NRP1 gene expression in PACA cells, thereby inhibiting cells proliferation and migration, which provides a basis for finding a valuable therapeutic target for PACA therapy.
Keywords: Neuropilin1; cell migration; cell proliferation; lentiviral interference; pancreatic cancer.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppression of the Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domain 7 and Inhibition of Migration and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Pancreatic Cancer PANC-1 Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(9):4065-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.9.4065. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 25987088
-
[Impact of the biological function on epithelial ovarian cancer with ITIH4 gene expression down-regulating in vitro].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Jan;48(1):34-40. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23531249 Chinese.
-
HOXB5 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of pancreatic cancer cell through the activation of the GSK3β/β-catenin pathway.Anticancer Drugs. 2020 Sep;31(8):828-835. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000948. Anticancer Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32796404
-
Effects of RNA interference-mediated NRP-1 silencing on the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Jul;12(1):513-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3405. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25738638
-
Neuropilin-1: A Multifaceted Target for Cancer Therapy.Curr Oncol. 2025 Mar 31;32(4):203. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32040203. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40277760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 15;12(12):1989. doi: 10.3390/genes12121989. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34946938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting CD44 and other pleiotropic co-receptors as a means for broad inhibition of tumor growth and metastasis.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Oct;41(5):599-611. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10292-4. Epub 2024 May 18. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 38761292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEUROD1 reinforces endocrine cell fate acquisition in pancreatic development.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 9;14(1):5554. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41306-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37689751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394‐424. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

